pacman::p_load("data.table", "dplyr", "tidyr",
"caret",
"ggplot2", "GGally",
"e1071")
titanic <- fread("../Titanic.csv") # 데이터 불러오기
titanic %>%
as_tibble4 Support Vector Machine with Linear Kernel
Support Vector Machine의 장점
- 분류 경계가 직사각형만 가능한 의사결정나무의 단점을 해결할 수 있다.
- 복잡한 비선형 결정 경계를 학습하는데 유용하다.
- 예측 변수에 분포를 가정하지 않는다.
Support Vector Machine의 단점
- 초모수가 매우 많으며, 초모수에 민감하다.
- 최적의 모형을 찾기 위해 다양한 커널과 초모수의 조합을 평가해야 한다.
- 모형 훈련이 느리다.
- 연속형 예측 변수만 가능하다.
- 범주형 예측 변수는 더미 또는 원-핫 인코딩 변환을 수행해야 한다.
- 해석하기 어려운 복잡한 블랙박스 모형이다.
실습 자료 : 1912년 4월 15일 타이타닉호 침몰 당시 탑승객들의 정보를 기록한 데이터셋이며, 총 11개의 변수를 포함하고 있다. 이 자료에서 Target은
Survived이다.

4.1 데이터 불러오기
# A tibble: 891 × 11
Survived Pclass Name Sex Age SibSp Parch Ticket Fare Cabin Embarked
<int> <int> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <int> <int> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <chr>
1 0 3 Braund, Mr. Owen Harris male 22 1 0 A/5 21171 7.25 "" S
2 1 1 Cumings, Mrs. John Bradley (Florence Briggs Thayer) female 38 1 0 PC 17599 71.3 "C85" C
3 1 3 Heikkinen, Miss. Laina female 26 0 0 STON/O2. 3101282 7.92 "" S
4 1 1 Futrelle, Mrs. Jacques Heath (Lily May Peel) female 35 1 0 113803 53.1 "C123" S
5 0 3 Allen, Mr. William Henry male 35 0 0 373450 8.05 "" S
6 0 3 Moran, Mr. James male NA 0 0 330877 8.46 "" Q
7 0 1 McCarthy, Mr. Timothy J male 54 0 0 17463 51.9 "E46" S
8 0 3 Palsson, Master. Gosta Leonard male 2 3 1 349909 21.1 "" S
9 1 3 Johnson, Mrs. Oscar W (Elisabeth Vilhelmina Berg) female 27 0 2 347742 11.1 "" S
10 1 2 Nasser, Mrs. Nicholas (Adele Achem) female 14 1 0 237736 30.1 "" C
# ℹ 881 more rows4.2 데이터 전처리 I
titanic %<>%
data.frame() %>% # Data Frame 형태로 변환
mutate(Survived = ifelse(Survived == 1, "yes", "no")) # Target을 문자형 변수로 변환
# 1. Convert to Factor
fac.col <- c("Pclass", "Sex",
# Target
"Survived")
titanic <- titanic %>%
mutate_at(fac.col, as.factor) # 범주형으로 변환
glimpse(titanic) # 데이터 구조 확인Rows: 891
Columns: 11
$ Survived <fct> no, yes, yes, yes, no, no, no, no, yes, yes, yes, yes, no, no, no, yes, no, yes, no, yes, no, yes, yes, yes, no, yes, no, no, yes, no, no, yes, yes, no, no, no, yes, no, no, yes, no…
$ Pclass <fct> 3, 1, 3, 1, 3, 3, 1, 3, 3, 2, 3, 1, 3, 3, 3, 2, 3, 2, 3, 3, 2, 2, 3, 1, 3, 3, 3, 1, 3, 3, 1, 1, 3, 2, 1, 1, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 2, 3, 2, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 1, 2, 1, 1, 2, 3, 2, 3, 3…
$ Name <chr> "Braund, Mr. Owen Harris", "Cumings, Mrs. John Bradley (Florence Briggs Thayer)", "Heikkinen, Miss. Laina", "Futrelle, Mrs. Jacques Heath (Lily May Peel)", "Allen, Mr. William Henry…
$ Sex <fct> male, female, female, female, male, male, male, male, female, female, female, female, male, male, female, female, male, male, female, female, male, male, female, male, female, femal…
$ Age <dbl> 22.0, 38.0, 26.0, 35.0, 35.0, NA, 54.0, 2.0, 27.0, 14.0, 4.0, 58.0, 20.0, 39.0, 14.0, 55.0, 2.0, NA, 31.0, NA, 35.0, 34.0, 15.0, 28.0, 8.0, 38.0, NA, 19.0, NA, NA, 40.0, NA, NA, 66.…
$ SibSp <int> 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 3, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 4, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 3, 1, 0, 3, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 2, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 4, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 5, 0…
$ Parch <int> 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 0, 0, 5, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 5, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 2, 2, 0…
$ Ticket <chr> "A/5 21171", "PC 17599", "STON/O2. 3101282", "113803", "373450", "330877", "17463", "349909", "347742", "237736", "PP 9549", "113783", "A/5. 2151", "347082", "350406", "248706", "38…
$ Fare <dbl> 7.2500, 71.2833, 7.9250, 53.1000, 8.0500, 8.4583, 51.8625, 21.0750, 11.1333, 30.0708, 16.7000, 26.5500, 8.0500, 31.2750, 7.8542, 16.0000, 29.1250, 13.0000, 18.0000, 7.2250, 26.0000,…
$ Cabin <chr> "", "C85", "", "C123", "", "", "E46", "", "", "", "G6", "C103", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "D56", "", "A6", "", "", "", "C23 C25 C27", "", "", "", "B78", "", "", "", "", ""…
$ Embarked <chr> "S", "C", "S", "S", "S", "Q", "S", "S", "S", "C", "S", "S", "S", "S", "S", "S", "Q", "S", "S", "C", "S", "S", "Q", "S", "S", "S", "C", "S", "Q", "S", "C", "C", "Q", "S", "C", "S", "…# 2. Generate New Variable
titanic <- titanic %>%
mutate(FamSize = SibSp + Parch) # "FamSize = 형제 및 배우자 수 + 부모님 및 자녀 수"로 가족 수를 의미하는 새로운 변수
glimpse(titanic) # 데이터 구조 확인Rows: 891
Columns: 12
$ Survived <fct> no, yes, yes, yes, no, no, no, no, yes, yes, yes, yes, no, no, no, yes, no, yes, no, yes, no, yes, yes, yes, no, yes, no, no, yes, no, no, yes, yes, no, no, no, yes, no, no, yes, no…
$ Pclass <fct> 3, 1, 3, 1, 3, 3, 1, 3, 3, 2, 3, 1, 3, 3, 3, 2, 3, 2, 3, 3, 2, 2, 3, 1, 3, 3, 3, 1, 3, 3, 1, 1, 3, 2, 1, 1, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 2, 3, 2, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 1, 2, 1, 1, 2, 3, 2, 3, 3…
$ Name <chr> "Braund, Mr. Owen Harris", "Cumings, Mrs. John Bradley (Florence Briggs Thayer)", "Heikkinen, Miss. Laina", "Futrelle, Mrs. Jacques Heath (Lily May Peel)", "Allen, Mr. William Henry…
$ Sex <fct> male, female, female, female, male, male, male, male, female, female, female, female, male, male, female, female, male, male, female, female, male, male, female, male, female, femal…
$ Age <dbl> 22.0, 38.0, 26.0, 35.0, 35.0, NA, 54.0, 2.0, 27.0, 14.0, 4.0, 58.0, 20.0, 39.0, 14.0, 55.0, 2.0, NA, 31.0, NA, 35.0, 34.0, 15.0, 28.0, 8.0, 38.0, NA, 19.0, NA, NA, 40.0, NA, NA, 66.…
$ SibSp <int> 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 3, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 4, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 3, 1, 0, 3, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 2, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 4, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 5, 0…
$ Parch <int> 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 0, 0, 5, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 5, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 2, 2, 0…
$ Ticket <chr> "A/5 21171", "PC 17599", "STON/O2. 3101282", "113803", "373450", "330877", "17463", "349909", "347742", "237736", "PP 9549", "113783", "A/5. 2151", "347082", "350406", "248706", "38…
$ Fare <dbl> 7.2500, 71.2833, 7.9250, 53.1000, 8.0500, 8.4583, 51.8625, 21.0750, 11.1333, 30.0708, 16.7000, 26.5500, 8.0500, 31.2750, 7.8542, 16.0000, 29.1250, 13.0000, 18.0000, 7.2250, 26.0000,…
$ Cabin <chr> "", "C85", "", "C123", "", "", "E46", "", "", "", "G6", "C103", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "D56", "", "A6", "", "", "", "C23 C25 C27", "", "", "", "B78", "", "", "", "", ""…
$ Embarked <chr> "S", "C", "S", "S", "S", "Q", "S", "S", "S", "C", "S", "S", "S", "S", "S", "S", "Q", "S", "S", "C", "S", "S", "Q", "S", "S", "S", "C", "S", "Q", "S", "C", "C", "Q", "S", "C", "S", "…
$ FamSize <int> 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 4, 2, 1, 2, 0, 0, 6, 0, 0, 5, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 4, 6, 0, 5, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 2, 1, 1, 1, 0, 3, 0, 0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 5, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 3, 7, 0…# 3. Select Variables used for Analysis
titanic1 <- titanic %>%
select(Survived, Pclass, Sex, Age, Fare, FamSize) # 분석에 사용할 변수 선택
# 4. Convert One-hot Encoding for 범주형 예측 변수
dummies <- dummyVars(formula = ~ ., # formula : ~ 예측 변수 / "." : data에 포함된 모든 변수를 의미
data = titanic1[,-1], # Dataset including Only 예측 변수 -> Target 제외
fullRank = FALSE) # fullRank = TRUE : Dummy Variable, fullRank = FALSE : One-hot Encoding
titanic.Var <- predict(dummies, newdata = titanic1) %>% # 범주형 예측 변수에 대한 One-hot Encoding 변환
data.frame() # Data Frame 형태로 변환
glimpse(titanic.Var) # 데이터 구조 확인Rows: 891
Columns: 8
$ Pclass.1 <dbl> 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0,…
$ Pclass.2 <dbl> 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0,…
$ Pclass.3 <dbl> 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1,…
$ Sex.female <dbl> 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0,…
$ Sex.male <dbl> 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1,…
$ Age <dbl> 22.0, 38.0, 26.0, 35.0, 35.0, NA, 54.0, 2.0, 27.0, 14.0, 4.0, 58.0, 20.0, 39.0, 14.0, 55.0, 2.0, NA, 31.0, NA, 35.0, 34.0, 15.0, 28.0, 8.0, 38.0, NA, 19.0, NA, NA, 40.0, NA, NA, 6…
$ Fare <dbl> 7.2500, 71.2833, 7.9250, 53.1000, 8.0500, 8.4583, 51.8625, 21.0750, 11.1333, 30.0708, 16.7000, 26.5500, 8.0500, 31.2750, 7.8542, 16.0000, 29.1250, 13.0000, 18.0000, 7.2250, 26.000…
$ FamSize <dbl> 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 4, 2, 1, 2, 0, 0, 6, 0, 0, 5, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 4, 6, 0, 5, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 2, 1, 1, 1, 0, 3, 0, 0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 5, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 3, 7,…# Combine Target with 변환된 예측 변수
titanic.df <- data.frame(Survived = titanic1$Survived,
titanic.Var)
titanic.df %>%
as_tibble# A tibble: 891 × 9
Survived Pclass.1 Pclass.2 Pclass.3 Sex.female Sex.male Age Fare FamSize
<fct> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 no 0 0 1 0 1 22 7.25 1
2 yes 1 0 0 1 0 38 71.3 1
3 yes 0 0 1 1 0 26 7.92 0
4 yes 1 0 0 1 0 35 53.1 1
5 no 0 0 1 0 1 35 8.05 0
6 no 0 0 1 0 1 NA 8.46 0
7 no 1 0 0 0 1 54 51.9 0
8 no 0 0 1 0 1 2 21.1 4
9 yes 0 0 1 1 0 27 11.1 2
10 yes 0 1 0 1 0 14 30.1 1
# ℹ 881 more rowsglimpse(titanic.df) # 데이터 구조 확인Rows: 891
Columns: 9
$ Survived <fct> no, yes, yes, yes, no, no, no, no, yes, yes, yes, yes, no, no, no, yes, no, yes, no, yes, no, yes, yes, yes, no, yes, no, no, yes, no, no, yes, yes, no, no, no, yes, no, no, yes, …
$ Pclass.1 <dbl> 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0,…
$ Pclass.2 <dbl> 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0,…
$ Pclass.3 <dbl> 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1,…
$ Sex.female <dbl> 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0,…
$ Sex.male <dbl> 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1,…
$ Age <dbl> 22.0, 38.0, 26.0, 35.0, 35.0, NA, 54.0, 2.0, 27.0, 14.0, 4.0, 58.0, 20.0, 39.0, 14.0, 55.0, 2.0, NA, 31.0, NA, 35.0, 34.0, 15.0, 28.0, 8.0, 38.0, NA, 19.0, NA, NA, 40.0, NA, NA, 6…
$ Fare <dbl> 7.2500, 71.2833, 7.9250, 53.1000, 8.0500, 8.4583, 51.8625, 21.0750, 11.1333, 30.0708, 16.7000, 26.5500, 8.0500, 31.2750, 7.8542, 16.0000, 29.1250, 13.0000, 18.0000, 7.2250, 26.000…
$ FamSize <dbl> 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 4, 2, 1, 2, 0, 0, 6, 0, 0, 5, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 4, 6, 0, 5, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 2, 1, 1, 1, 0, 3, 0, 0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 5, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 3, 7,…4.3 데이터 탐색
ggpairs(titanic.df,
aes(colour = Survived)) + # Target의 범주에 따라 색깔을 다르게 표현
theme_bw()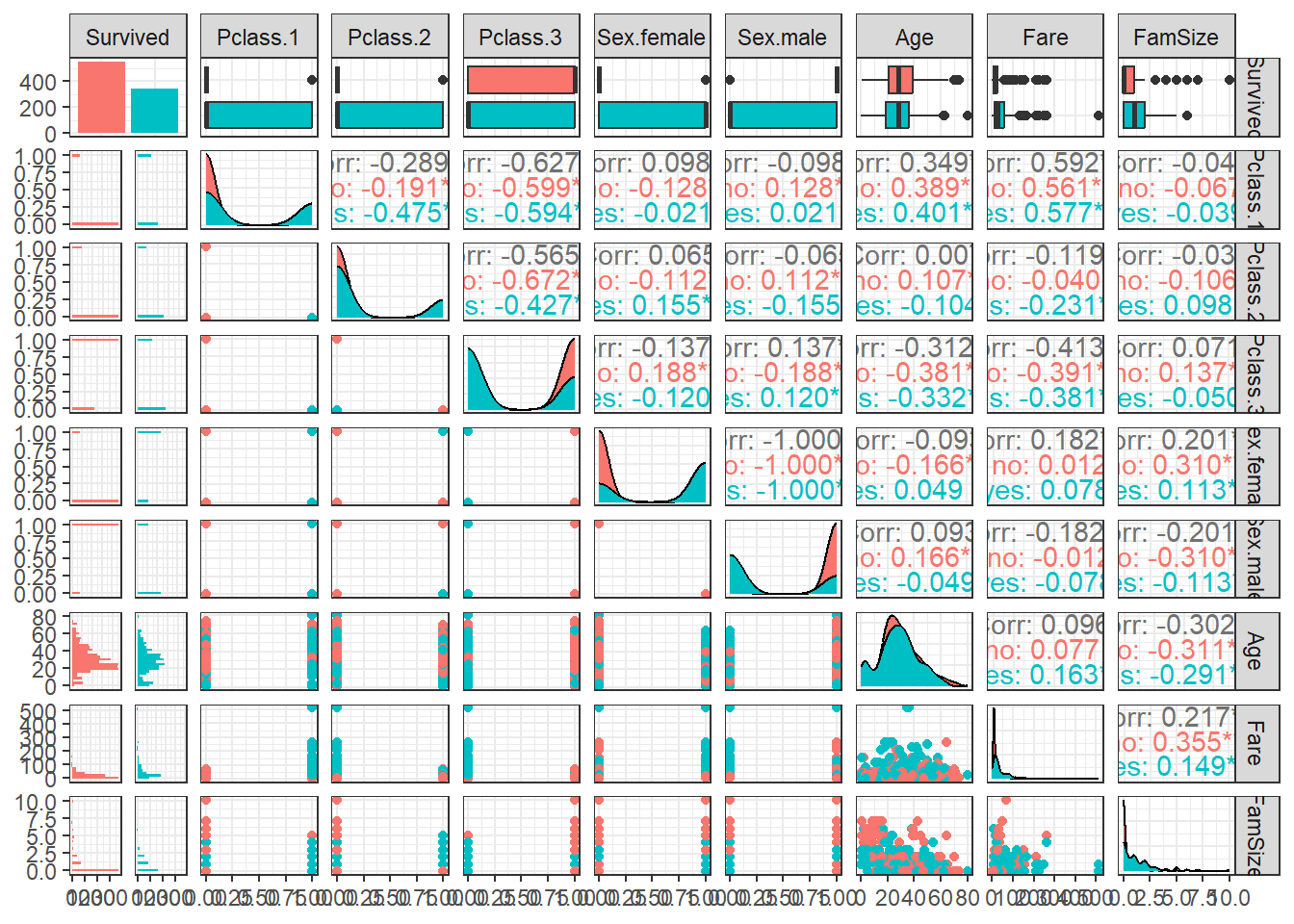
ggpairs(titanic.df,
aes(colour = Survived, alpha = 0.8)) + # Target의 범주에 따라 색깔을 다르게 표현
scale_colour_manual(values = c("purple", "cyan4")) + # 특정 색깔 지정
scale_fill_manual(values = c("purple", "cyan4")) + # 특정 색깔 지정
theme_bw()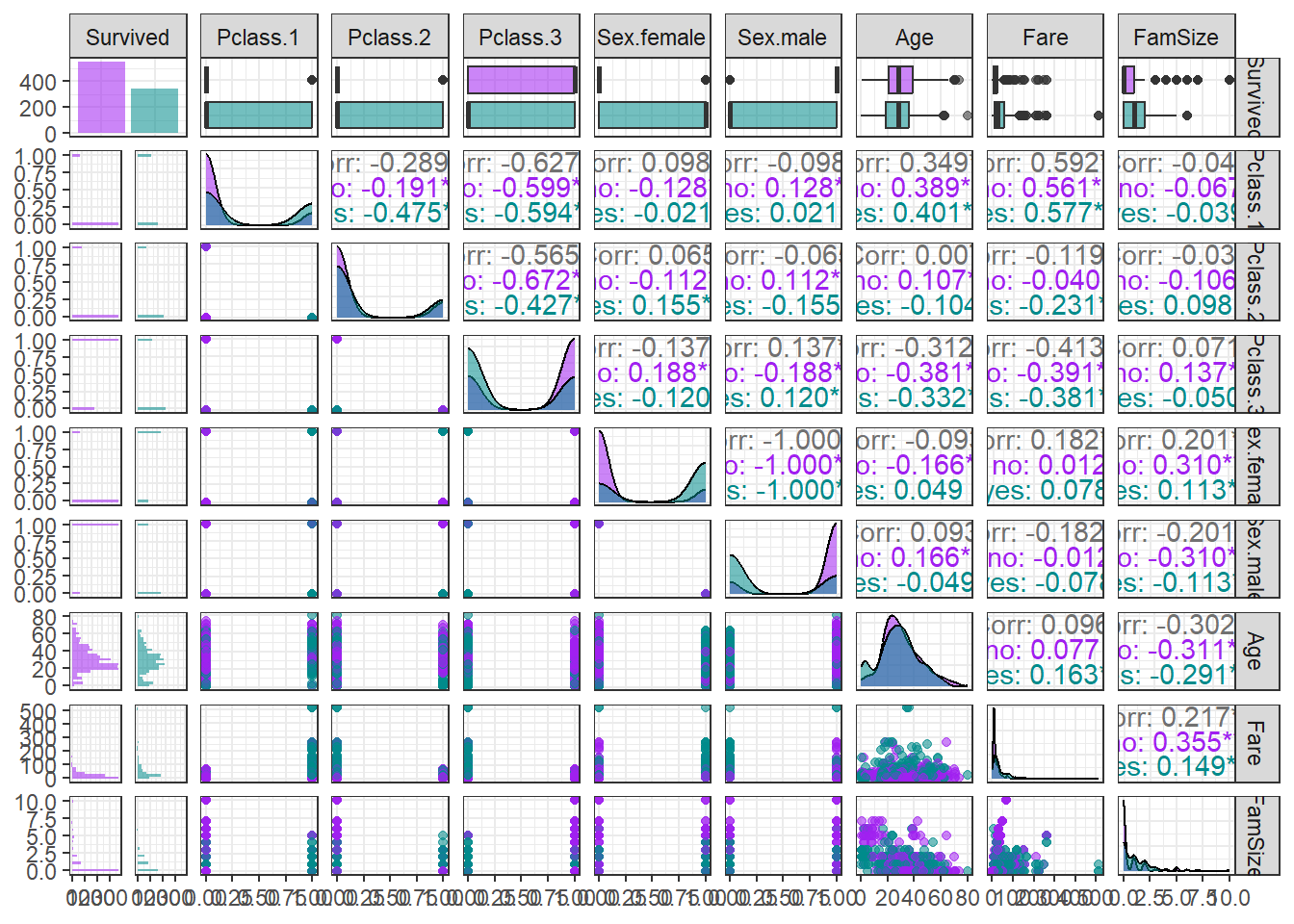
4.4 데이터 분할
# Partition (Training Dataset : Test Dataset = 7:3)
y <- titanic.df$Survived # Target
set.seed(200)
ind <- createDataPartition(y, p = 0.7, list =T) # Index를 이용하여 7:3으로 분할
titanic.trd <- titanic.df[ind$Resample1,] # Training Dataset
titanic.ted <- titanic.df[-ind$Resample1,] # Test Dataset4.5 데이터 전처리 II
# 1. Imputation
titanic.trd.Imp <- titanic.trd %>%
mutate(Age = replace_na(Age, mean(Age, na.rm = TRUE))) # 평균으로 결측값 대체
titanic.ted.Imp <- titanic.ted %>%
mutate(Age = replace_na(Age, mean(titanic.trd$Age, na.rm = TRUE))) # Training Dataset을 이용하여 결측값 대체
# 2. Standardization
preProcValues <- preProcess(titanic.trd.Imp,
method = c("center", "scale")) # Standardization 정의 -> Training Dataset에 대한 평균과 표준편차 계산
titanic.trd.Imp <- predict(preProcValues, titanic.trd.Imp) # Standardization for Training Dataset
titanic.ted.Imp <- predict(preProcValues, titanic.ted.Imp) # Standardization for Test Dataset
glimpse(titanic.trd.Imp) # 데이터 구조 확인Rows: 625
Columns: 9
$ Survived <fct> no, yes, yes, no, no, no, yes, yes, yes, yes, no, no, yes, no, yes, no, yes, no, no, no, yes, no, no, yes, yes, no, no, no, no, no, yes, no, no, no, yes, no, yes, no, no, no, yes,…
$ Pclass.1 <dbl> -0.593506, -0.593506, 1.682207, -0.593506, -0.593506, -0.593506, -0.593506, -0.593506, -0.593506, 1.682207, -0.593506, -0.593506, -0.593506, -0.593506, -0.593506, -0.593506, 1.682…
$ Pclass.2 <dbl> -0.4694145, -0.4694145, -0.4694145, -0.4694145, -0.4694145, -0.4694145, -0.4694145, 2.1269048, -0.4694145, -0.4694145, -0.4694145, -0.4694145, 2.1269048, -0.4694145, -0.4694145, 2…
$ Pclass.3 <dbl> 0.888575, 0.888575, -1.123597, 0.888575, 0.888575, 0.888575, 0.888575, -1.123597, 0.888575, -1.123597, 0.888575, 0.888575, -1.123597, 0.888575, 0.888575, -1.123597, -1.123597, 0.8…
$ Sex.female <dbl> -0.7572241, 1.3184999, 1.3184999, -0.7572241, -0.7572241, -0.7572241, 1.3184999, 1.3184999, 1.3184999, 1.3184999, -0.7572241, 1.3184999, -0.7572241, 1.3184999, 1.3184999, -0.75722…
$ Sex.male <dbl> 0.7572241, -1.3184999, -1.3184999, 0.7572241, 0.7572241, 0.7572241, -1.3184999, -1.3184999, -1.3184999, -1.3184999, 0.7572241, -1.3184999, 0.7572241, -1.3184999, -1.3184999, 0.757…
$ Age <dbl> -0.61306970, -0.30411628, 0.39102893, 0.39102893, 0.00000000, -2.15783684, -0.22687792, -1.23097656, -2.00336012, 2.16751113, 0.69998236, -1.23097656, 0.00000000, 0.08207551, 0.00…
$ Fare <dbl> -0.51776394, -0.50463325, 0.37414970, -0.50220165, -0.49425904, -0.24882814, -0.44222264, -0.07383411, -0.33393441, -0.14232374, -0.05040897, -0.50601052, -0.40590999, -0.30864569…
$ FamSize <dbl> 0.04506631, -0.55421976, 0.04506631, -0.55421976, -0.55421976, 1.84292454, 0.64435239, 0.04506631, 0.64435239, -0.55421976, 3.04149669, -0.55421976, -0.55421976, 0.04506631, -0.55…glimpse(titanic.ted.Imp) # 데이터 구조 확인Rows: 266
Columns: 9
$ Survived <fct> yes, no, no, yes, no, yes, yes, yes, yes, yes, no, no, yes, yes, no, yes, no, yes, yes, no, yes, no, no, no, no, no, no, yes, yes, no, no, no, no, no, no, no, no, no, no, yes, no,…
$ Pclass.1 <dbl> 1.682207, 1.682207, -0.593506, -0.593506, -0.593506, -0.593506, -0.593506, -0.593506, -0.593506, -0.593506, -0.593506, -0.593506, -0.593506, -0.593506, -0.593506, -0.593506, 1.682…
$ Pclass.2 <dbl> -0.4694145, -0.4694145, -0.4694145, 2.1269048, -0.4694145, 2.1269048, -0.4694145, -0.4694145, -0.4694145, 2.1269048, -0.4694145, -0.4694145, 2.1269048, 2.1269048, -0.4694145, 2.12…
$ Pclass.3 <dbl> -1.123597, -1.123597, 0.888575, -1.123597, 0.888575, -1.123597, 0.888575, 0.888575, 0.888575, -1.123597, 0.888575, 0.888575, -1.123597, -1.123597, 0.888575, -1.123597, -1.123597, …
$ Sex.female <dbl> 1.3184999, -0.7572241, -0.7572241, 1.3184999, -0.7572241, -0.7572241, 1.3184999, 1.3184999, -0.7572241, 1.3184999, -0.7572241, -0.7572241, 1.3184999, 1.3184999, -0.7572241, 1.3184…
$ Sex.male <dbl> -1.3184999, 0.7572241, 0.7572241, -1.3184999, 0.7572241, 0.7572241, -1.3184999, -1.3184999, 0.7572241, -1.3184999, 0.7572241, 0.7572241, -1.3184999, -1.3184999, 0.7572241, -1.3184…
$ Age <dbl> 0.62274400, 1.85855771, -0.76754642, 1.93579607, -2.15783684, 0.31379058, -1.15373820, 0.62274400, 0.00000000, -2.08059848, 0.00000000, -0.69030806, -0.07240121, -0.69030806, -0.1…
$ Fare <dbl> 0.727866891, 0.350076786, -0.502201647, -0.347551409, -0.092232621, -0.405909990, -0.502606266, -0.048220525, -0.518168555, 0.150037190, -0.502201647, -0.507064862, -0.153022808, …
$ FamSize <dbl> 0.04506631, -0.55421976, -0.55421976, -0.55421976, 2.44221062, -0.55421976, -0.55421976, 3.04149669, -0.55421976, 1.24363847, -0.55421976, -0.55421976, 0.04506631, -0.55421976, -0…4.6 모형 훈련
Package "e1071"는 Support Vector Machine을 효율적으로 구현할 수 있는 “libsvm”을 R에서 사용할 수 있도록 만든 Package이며, 함수 svm()을 이용하여 Support Vector Machine을 수행할 수 있다. 함수에서 사용할 수 있는 자세한 옵션은 여기를 참고한다.
svm(formula, data, kernel, cost, probability, ...)formula: Target과 예측 변수의 관계를 표현하기 위한 함수로써 일반적으로Target ~ 예측 변수의 형태로 표현한다.data:formula에 포함하고 있는 변수들의 데이터셋(Data Frame)kernel: Kernel 함수"linear": \(k(\boldsymbol{x}, \boldsymbol{x}') = \boldsymbol{x}\boldsymbol{x}'\)"polynomial": \(k(\boldsymbol{x}, \boldsymbol{x}') = (\gamma \boldsymbol{x}\boldsymbol{x}' + \text{coef0})^{\text{degree}}\)"radial": \(k(\boldsymbol{x}, \boldsymbol{x}') = \exp\left(-\gamma||\boldsymbol{x}-\boldsymbol{x}'||^2 \right)\)"sigmoid": \(k(\boldsymbol{x}, \boldsymbol{x}') = tanh(\gamma \boldsymbol{x}\boldsymbol{x}' + \text{coef0})\)
cost: 데이터를 잘못 분류하는 선을 그을 경우 지불해야 할 costprobability:Test Dataset에 대한예측 확률의 생성 여부TRUE: 함수predict()를 이용하여Test Dataset에 대한예측 확률을 생성할 수 있다.
svm.model.li <- svm(Survived ~.,
data = titanic.trd.Imp,
kernel = "linear",
cost = 1,
probability = TRUE)
summary(svm.model.li)
Call:
svm(formula = Survived ~ ., data = titanic.trd.Imp, kernel = "linear", cost = 1, probability = TRUE)
Parameters:
SVM-Type: C-classification
SVM-Kernel: linear
cost: 1
Number of Support Vectors: 287
( 143 144 )
Number of Classes: 2
Levels:
no yesResult! Number of Support Vectors는 결정경계와 가까이 위치한 case의 수이다. 해당 데이터에서는 총 287개의 case로, "Survived = no"에 해당하는 case는 143개, "Survived = yes"에 해당하는 case는 144개이다. case의 행 번호는 svm.model.li$index를 이용하여 확인할 수 있다.
# Support Vector Index
svm.model.li$index [1] 12 14 16 18 20 23 27 30 32 33 39 48 50 59 71 76 77 79 80 83 93 94 95 100 112 114 119 121 122 129 135 140 146 151 156 157 160 161 164 166 170 173 176 181 182 190 193 201
[49] 202 203 205 229 232 234 237 238 243 252 261 270 281 283 287 291 293 305 307 315 321 330 336 340 344 346 347 348 349 351 359 367 371 373 376 377 379 384 389 393 395 397 401 402 405 408 416 423
[97] 429 436 447 448 451 464 466 467 470 471 478 479 493 499 508 513 514 515 517 521 525 538 539 543 550 554 556 557 558 563 564 568 571 573 574 577 581 591 598 599 607 608 610 620 622 623 625 7
[145] 9 13 15 17 21 25 31 37 43 52 55 56 57 58 61 74 75 86 87 88 92 97 99 116 123 124 125 130 134 139 155 163 165 171 172 180 187 188 189 191 195 197 206 208 212 223 226 228
[193] 233 235 240 241 249 255 256 258 266 275 276 279 284 290 294 302 303 304 308 312 313 316 317 318 320 326 334 335 352 353 355 357 358 362 372 375 378 382 388 390 391 399 400 406 407 411 421 422
[241] 424 426 427 431 434 437 439 440 445 446 455 456 457 459 463 468 474 475 480 485 487 492 496 498 500 509 511 518 524 527 530 535 536 553 565 566 576 578 582 583 584 589 600 602 603 609 6124.7 모형 평가
Caution! 모형 평가를 위해 Test Dataset에 대한 예측 class/확률 이 필요하며, 함수 predict()를 이용하여 생성한다.
# 예측 class 생성
svm.li.pred <- predict(svm.model.li,
newdata = titanic.ted.Imp[,-1], # Test Dataset including Only 예측 변수
type = "class") # 예측 class 생성
svm.li.pred %>%
as_tibble# A tibble: 266 × 1
value
<fct>
1 yes
2 no
3 no
4 yes
5 no
6 no
7 yes
8 no
9 no
10 yes
# ℹ 256 more rows4.7.1 ConfusionMatrix
CM <- caret::confusionMatrix(svm.li.pred, titanic.ted.Imp$Survived,
positive = "yes") # confusionMatrix(예측 class, 실제 class, positive="관심 class")
CMConfusion Matrix and Statistics
Reference
Prediction no yes
no 150 34
yes 14 68
Accuracy : 0.8195
95% CI : (0.768, 0.8638)
No Information Rate : 0.6165
P-Value [Acc > NIR] : 5.675e-13
Kappa : 0.6037
Mcnemar's Test P-Value : 0.006099
Sensitivity : 0.6667
Specificity : 0.9146
Pos Pred Value : 0.8293
Neg Pred Value : 0.8152
Prevalence : 0.3835
Detection Rate : 0.2556
Detection Prevalence : 0.3083
Balanced Accuracy : 0.7907
'Positive' Class : yes
4.7.2 ROC 곡선
# 예측 확률 생성
test.svm.prob <- predict(svm.model.li,
newdata = titanic.ted.Imp[,-1], # Test Dataset including Only 예측 변수
probability = TRUE) # 예측 확률 생성
attr(test.svm.prob, "probabilities") %>%
as_tibble# A tibble: 266 × 2
no yes
<dbl> <dbl>
1 0.227 0.773
2 0.785 0.215
3 0.807 0.193
4 0.288 0.712
5 0.921 0.0794
6 0.799 0.201
7 0.242 0.758
8 0.648 0.352
9 0.825 0.175
10 0.303 0.697
# ℹ 256 more rowstest.svm.prob <- attr(test.svm.prob, "probabilities")[,2] # "Survived = yes"에 대한 예측 확률
ac <- titanic.ted.Imp$Survived # Test Dataset의 실제 class
pp <- as.numeric(test.svm.prob) # 예측 확률을 수치형으로 변환4.7.2.1 Package “pROC”
pacman::p_load("pROC")
svm.roc <- roc(ac, pp, plot = T, col = "gray") # roc(실제 class, 예측 확률)
auc <- round(auc(svm.roc), 3)
legend("bottomright", legend = auc, bty = "n")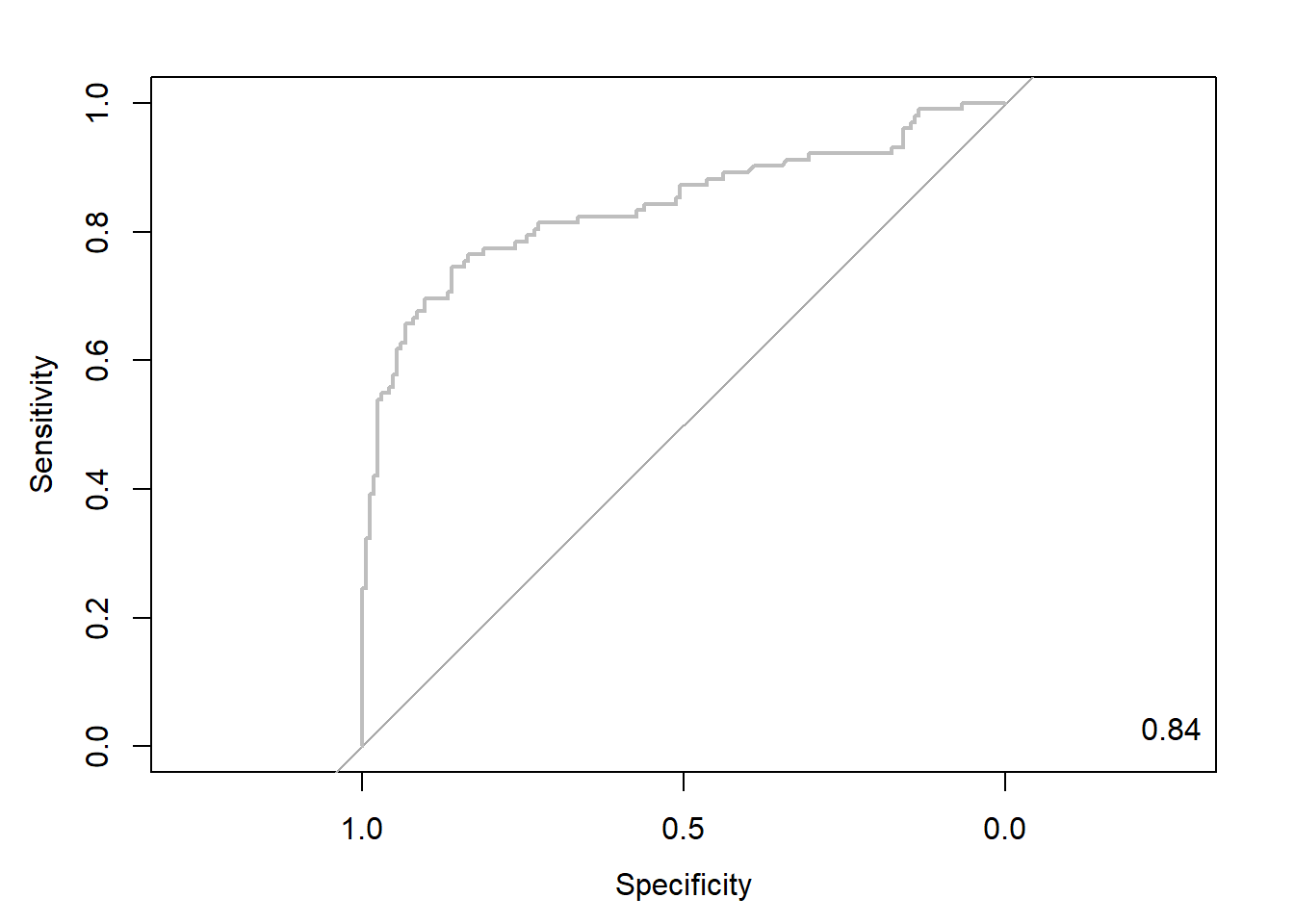
Caution! Package "pROC"를 통해 출력한 ROC 곡선은 다양한 함수를 이용해서 그래프를 수정할 수 있다.
# 함수 plot.roc() 이용
plot.roc(svm.roc,
col="gray", # Line Color
print.auc = TRUE, # AUC 출력 여부
print.auc.col = "red", # AUC 글씨 색깔
print.thres = TRUE, # Cutoff Value 출력 여부
print.thres.pch = 19, # Cutoff Value를 표시하는 도형 모양
print.thres.col = "red", # Cutoff Value를 표시하는 도형의 색깔
auc.polygon = TRUE, # 곡선 아래 면적에 대한 여부
auc.polygon.col = "gray90") # 곡선 아래 면적의 색깔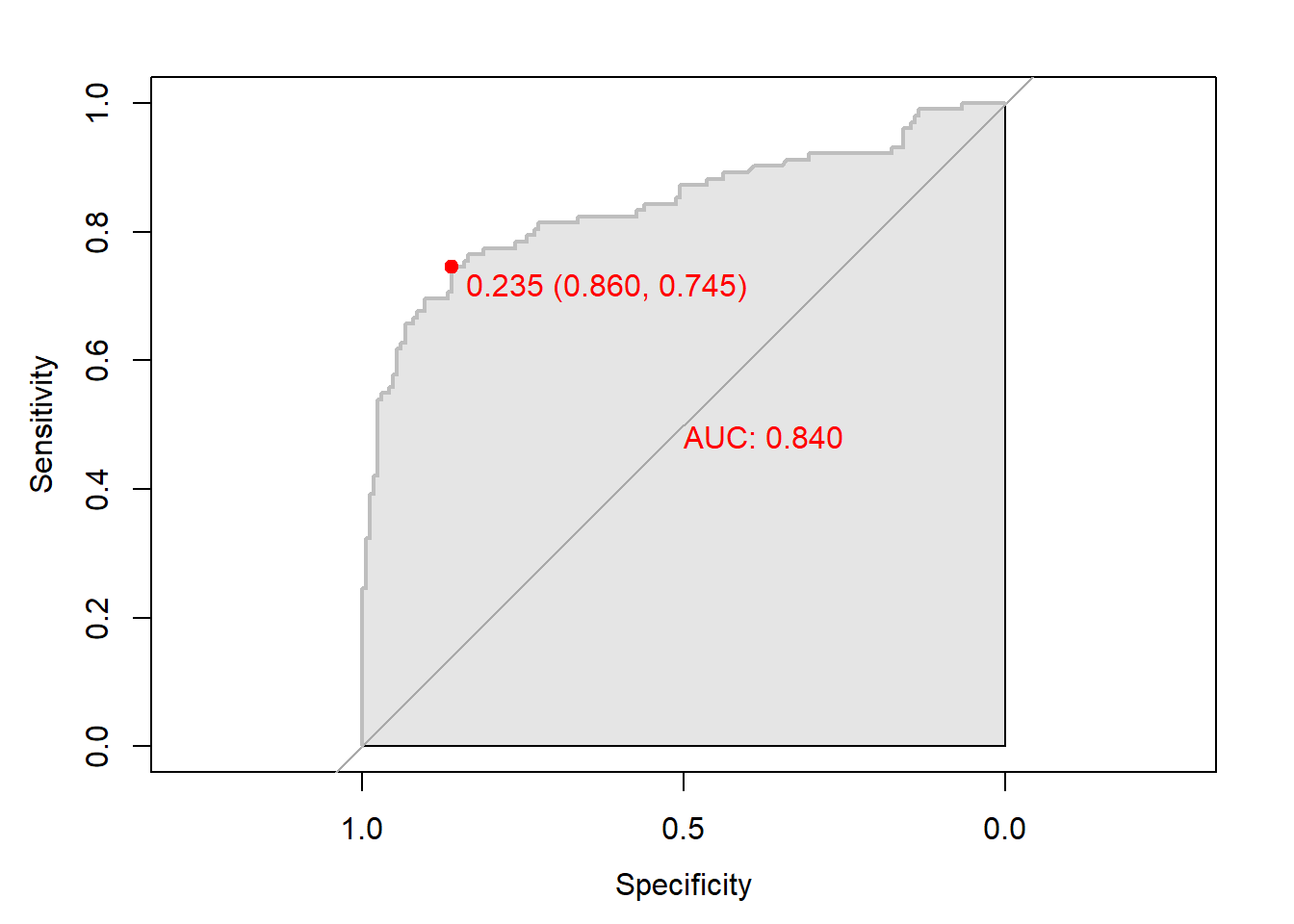
# 함수 ggroc() 이용
ggroc(svm.roc) +
annotate(geom = "text", x = 0.9, y = 1.0,
label = paste("AUC = ", auc),
size = 5,
color="red") +
theme_bw()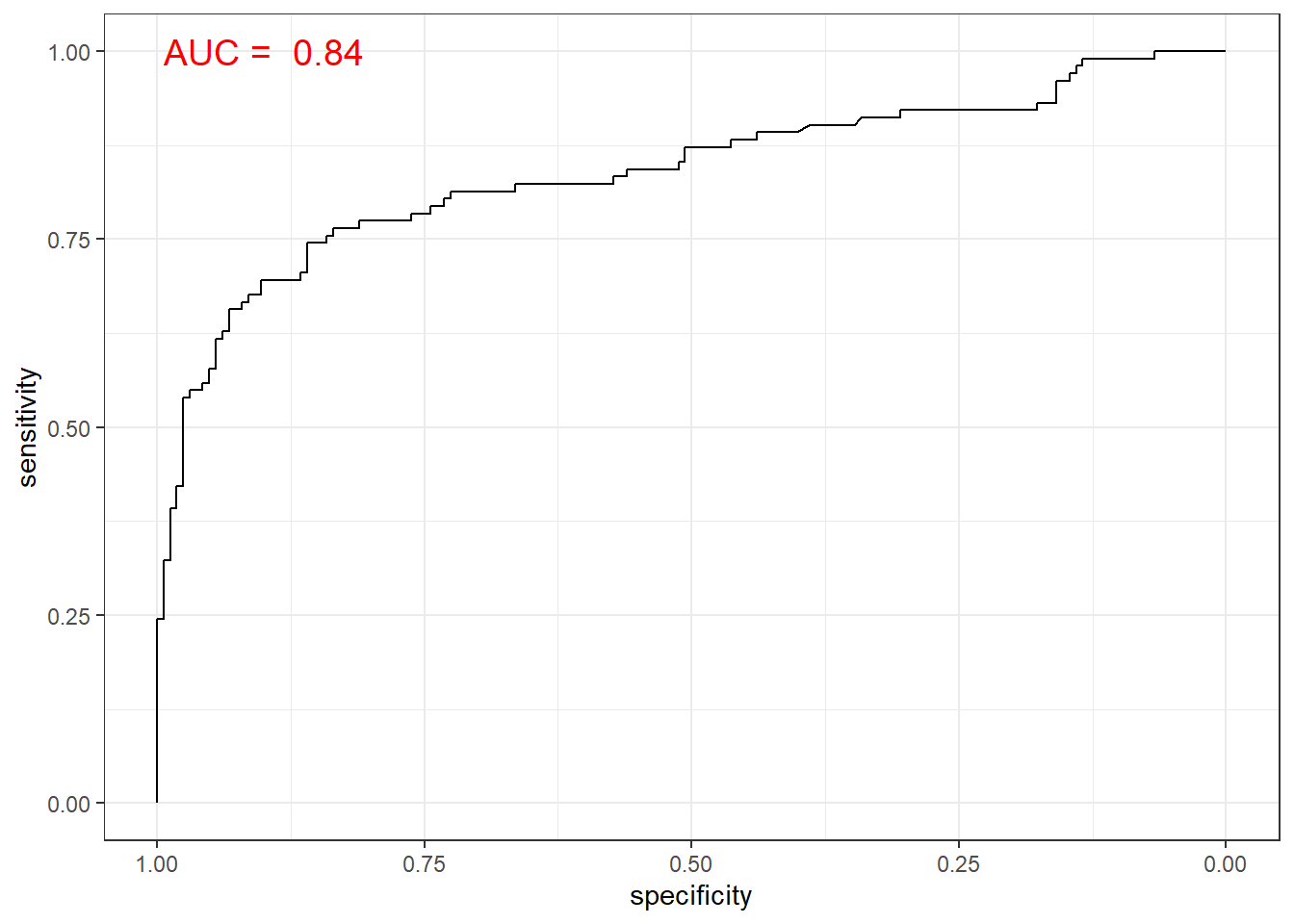
4.7.2.2 Package “Epi”
pacman::p_load("Epi")
# install_version("etm", version = "1.1", repos = "http://cran.us.r-project.org")
ROC(pp, ac, plot = "ROC") # ROC(예측 확률, 실제 class) 
4.7.2.3 Package “ROCR”
pacman::p_load("ROCR")
svm.pred <- prediction(pp, ac) # prediction(예측 확률, 실제 class)
svm.perf <- performance(svm.pred, "tpr", "fpr") # performance(, "민감도", "1-특이도")
plot(svm.perf, col = "gray") # ROC Curve
perf.auc <- performance(svm.pred, "auc") # AUC
auc <- attributes(perf.auc)$y.values
legend("bottomright", legend = auc, bty = "n")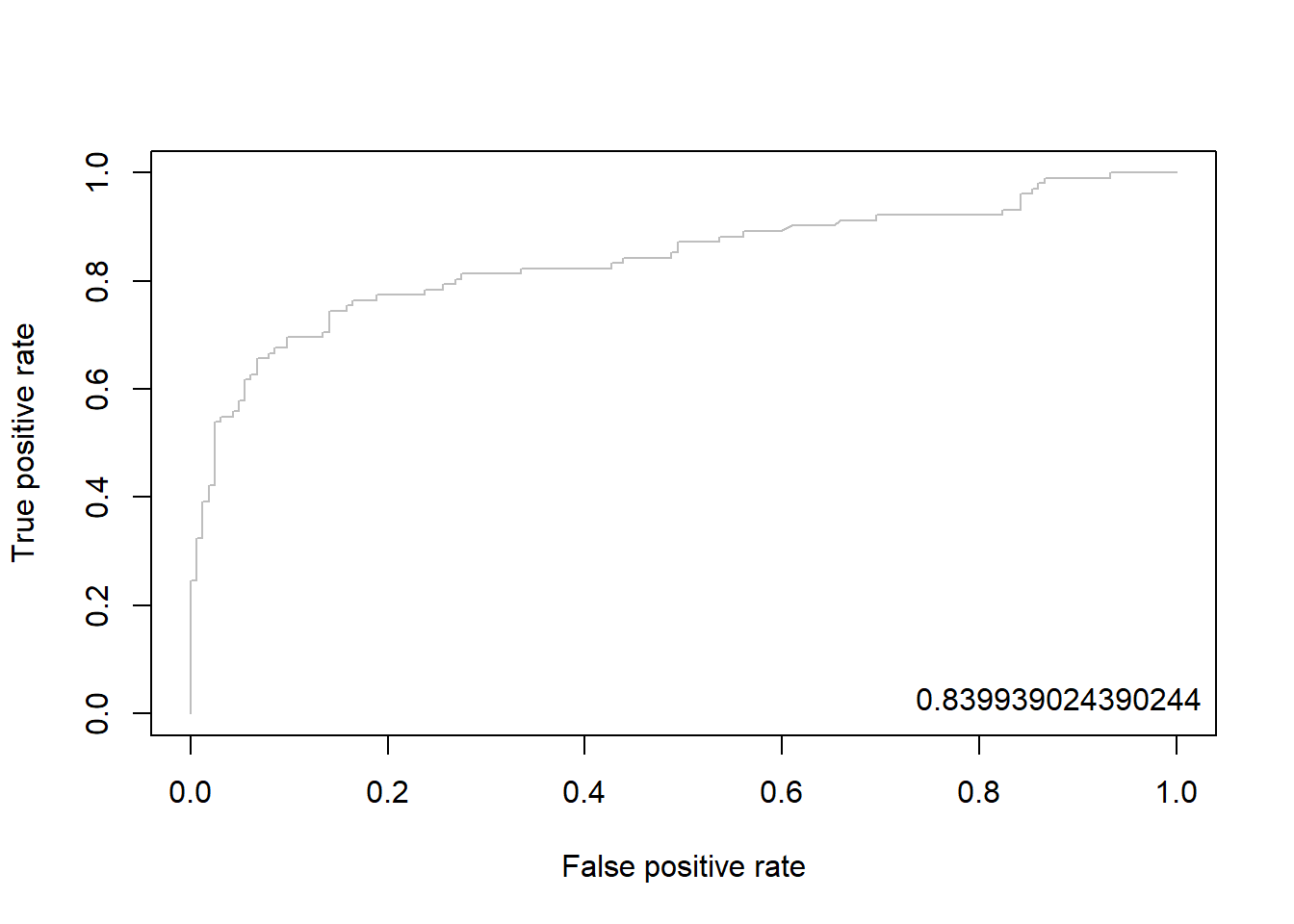
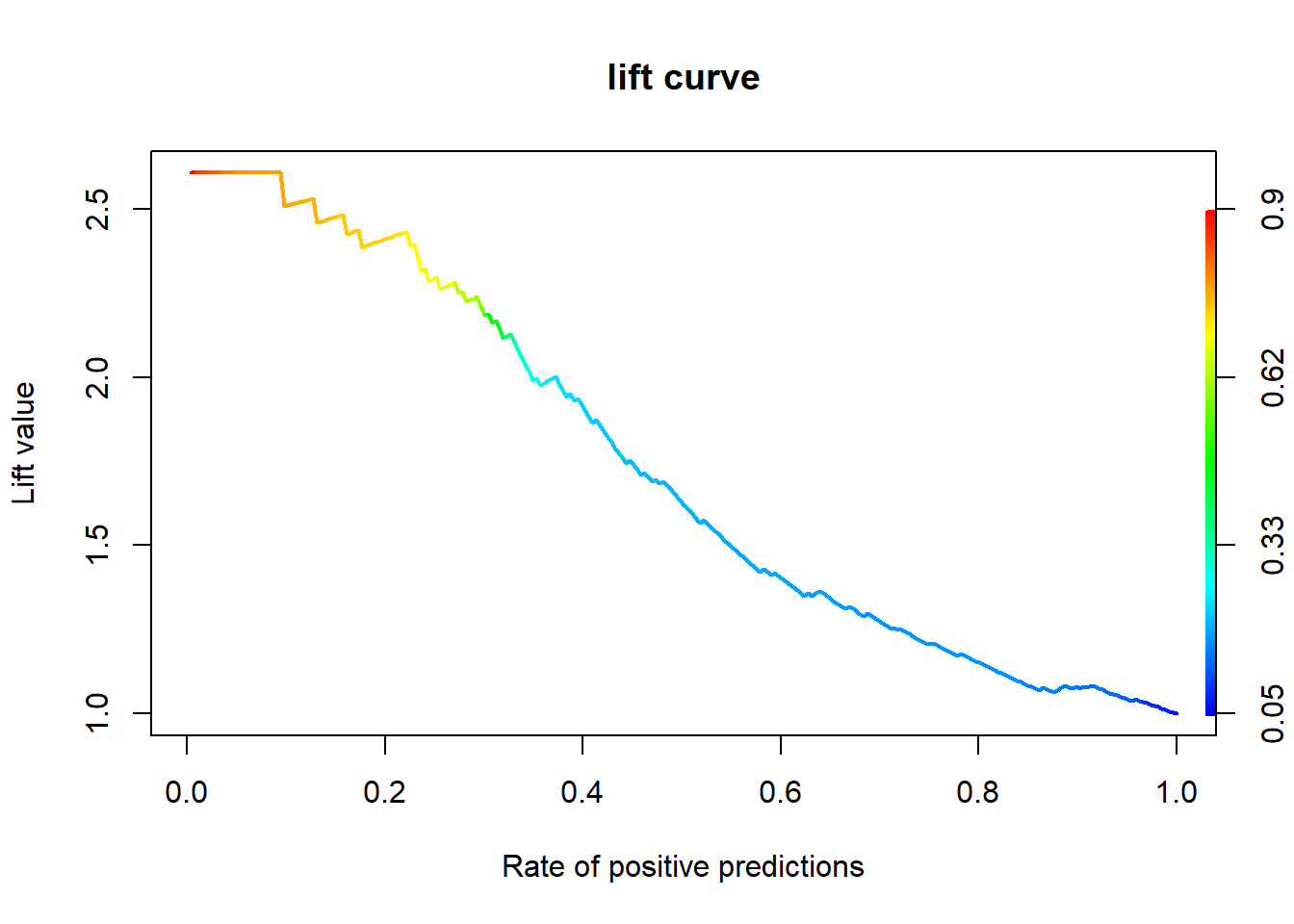
4.7.3 향상 차트
4.7.3.1 Package “ROCR”
svm.perf <- performance(svm.pred, "lift", "rpp") # Lift Chart
plot(svm.perf, main = "lift curve",
colorize = T, # Coloring according to cutoff
lwd = 2)