pacman::p_load("data.table",
"tidyverse",
"dplyr", "tidyr",
"ggplot2", "GGally",
"caret",
"doParallel", "parallel") # For 병렬 처리
registerDoParallel(cores=detectCores()) # 사용할 Core 개수 지정
titanic <- fread("../Titanic.csv") # 데이터 불러오기
titanic %>%
as_tibble12 Gradient Boosting
Gradient Boosting의 장점
- 예측 성능이 높다.
- 다양한 손실함수를 최적화할 수 있다.
Gradient Boosting의 단점
- 이상치에 민감하다.
- 과적합이 빠르게 발생할 수 있다.
- 병렬 처리가 지원되지 않아 대용량 데이터셋의 경우 매우 많은 시간이 필요하다.
- 수행시간이 오래 걸린다.
실습 자료 : 1912년 4월 15일 타이타닉호 침몰 당시 탑승객들의 정보를 기록한 데이터셋이며, 총 11개의 변수를 포함하고 있다. 이 자료에서 Target은
Survived이다.
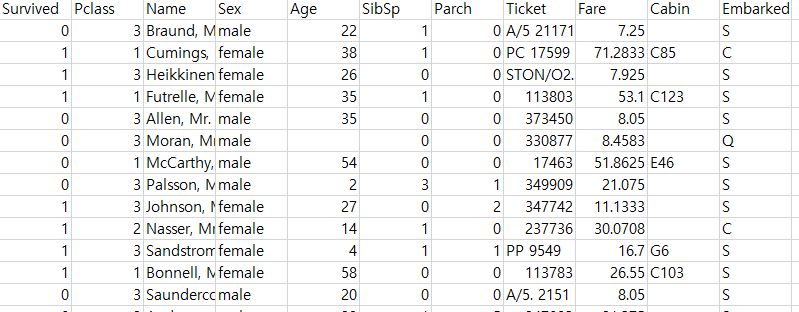

12.1 데이터 불러오기
# A tibble: 891 × 11
Survived Pclass Name Sex Age SibSp Parch Ticket Fare Cabin Embarked
<int> <int> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <int> <int> <chr> <dbl> <chr> <chr>
1 0 3 Braund, Mr. Owen Harris male 22 1 0 A/5 21171 7.25 "" S
2 1 1 Cumings, Mrs. John Bradley (Florence Briggs Thayer) female 38 1 0 PC 17599 71.3 "C85" C
3 1 3 Heikkinen, Miss. Laina female 26 0 0 STON/O2. 3101282 7.92 "" S
4 1 1 Futrelle, Mrs. Jacques Heath (Lily May Peel) female 35 1 0 113803 53.1 "C123" S
5 0 3 Allen, Mr. William Henry male 35 0 0 373450 8.05 "" S
6 0 3 Moran, Mr. James male NA 0 0 330877 8.46 "" Q
7 0 1 McCarthy, Mr. Timothy J male 54 0 0 17463 51.9 "E46" S
8 0 3 Palsson, Master. Gosta Leonard male 2 3 1 349909 21.1 "" S
9 1 3 Johnson, Mrs. Oscar W (Elisabeth Vilhelmina Berg) female 27 0 2 347742 11.1 "" S
10 1 2 Nasser, Mrs. Nicholas (Adele Achem) female 14 1 0 237736 30.1 "" C
# ℹ 881 more rows12.2 데이터 전처리 I
titanic %<>%
data.frame() %>% # Data Frame 형태로 변환
mutate(Survived = ifelse(Survived == 1, "yes", "no")) # Target을 문자형 변수로 변환
# 1. Convert to Factor
fac.col <- c("Pclass", "Sex",
# Target
"Survived")
titanic <- titanic %>%
mutate_at(fac.col, as.factor) # 범주형으로 변환
glimpse(titanic) # 데이터 구조 확인Rows: 891
Columns: 11
$ Survived <fct> no, yes, yes, yes, no, no, no, no, yes, yes, yes, yes, no, no, no, yes, no, yes, no, yes, no, yes, yes, yes, no, yes, no, no, yes, no, no, yes, yes, no, no, no, yes, no, no, yes, no…
$ Pclass <fct> 3, 1, 3, 1, 3, 3, 1, 3, 3, 2, 3, 1, 3, 3, 3, 2, 3, 2, 3, 3, 2, 2, 3, 1, 3, 3, 3, 1, 3, 3, 1, 1, 3, 2, 1, 1, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 2, 3, 2, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 1, 2, 1, 1, 2, 3, 2, 3, 3…
$ Name <chr> "Braund, Mr. Owen Harris", "Cumings, Mrs. John Bradley (Florence Briggs Thayer)", "Heikkinen, Miss. Laina", "Futrelle, Mrs. Jacques Heath (Lily May Peel)", "Allen, Mr. William Henry…
$ Sex <fct> male, female, female, female, male, male, male, male, female, female, female, female, male, male, female, female, male, male, female, female, male, male, female, male, female, femal…
$ Age <dbl> 22.0, 38.0, 26.0, 35.0, 35.0, NA, 54.0, 2.0, 27.0, 14.0, 4.0, 58.0, 20.0, 39.0, 14.0, 55.0, 2.0, NA, 31.0, NA, 35.0, 34.0, 15.0, 28.0, 8.0, 38.0, NA, 19.0, NA, NA, 40.0, NA, NA, 66.…
$ SibSp <int> 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 3, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 4, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 3, 1, 0, 3, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 2, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 4, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 5, 0…
$ Parch <int> 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 0, 0, 5, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 5, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 2, 2, 0…
$ Ticket <chr> "A/5 21171", "PC 17599", "STON/O2. 3101282", "113803", "373450", "330877", "17463", "349909", "347742", "237736", "PP 9549", "113783", "A/5. 2151", "347082", "350406", "248706", "38…
$ Fare <dbl> 7.2500, 71.2833, 7.9250, 53.1000, 8.0500, 8.4583, 51.8625, 21.0750, 11.1333, 30.0708, 16.7000, 26.5500, 8.0500, 31.2750, 7.8542, 16.0000, 29.1250, 13.0000, 18.0000, 7.2250, 26.0000,…
$ Cabin <chr> "", "C85", "", "C123", "", "", "E46", "", "", "", "G6", "C103", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "D56", "", "A6", "", "", "", "C23 C25 C27", "", "", "", "B78", "", "", "", "", ""…
$ Embarked <chr> "S", "C", "S", "S", "S", "Q", "S", "S", "S", "C", "S", "S", "S", "S", "S", "S", "Q", "S", "S", "C", "S", "S", "Q", "S", "S", "S", "C", "S", "Q", "S", "C", "C", "Q", "S", "C", "S", "…# 2. Generate New Variable
titanic <- titanic %>%
mutate(FamSize = SibSp + Parch) # "FamSize = 형제 및 배우자 수 + 부모님 및 자녀 수"로 가족 수를 의미하는 새로운 변수
glimpse(titanic) # 데이터 구조 확인Rows: 891
Columns: 12
$ Survived <fct> no, yes, yes, yes, no, no, no, no, yes, yes, yes, yes, no, no, no, yes, no, yes, no, yes, no, yes, yes, yes, no, yes, no, no, yes, no, no, yes, yes, no, no, no, yes, no, no, yes, no…
$ Pclass <fct> 3, 1, 3, 1, 3, 3, 1, 3, 3, 2, 3, 1, 3, 3, 3, 2, 3, 2, 3, 3, 2, 2, 3, 1, 3, 3, 3, 1, 3, 3, 1, 1, 3, 2, 1, 1, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 2, 3, 2, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 1, 2, 1, 1, 2, 3, 2, 3, 3…
$ Name <chr> "Braund, Mr. Owen Harris", "Cumings, Mrs. John Bradley (Florence Briggs Thayer)", "Heikkinen, Miss. Laina", "Futrelle, Mrs. Jacques Heath (Lily May Peel)", "Allen, Mr. William Henry…
$ Sex <fct> male, female, female, female, male, male, male, male, female, female, female, female, male, male, female, female, male, male, female, female, male, male, female, male, female, femal…
$ Age <dbl> 22.0, 38.0, 26.0, 35.0, 35.0, NA, 54.0, 2.0, 27.0, 14.0, 4.0, 58.0, 20.0, 39.0, 14.0, 55.0, 2.0, NA, 31.0, NA, 35.0, 34.0, 15.0, 28.0, 8.0, 38.0, NA, 19.0, NA, NA, 40.0, NA, NA, 66.…
$ SibSp <int> 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 3, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 4, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 3, 1, 0, 3, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 2, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 4, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 5, 0…
$ Parch <int> 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 0, 0, 5, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 5, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 2, 2, 0…
$ Ticket <chr> "A/5 21171", "PC 17599", "STON/O2. 3101282", "113803", "373450", "330877", "17463", "349909", "347742", "237736", "PP 9549", "113783", "A/5. 2151", "347082", "350406", "248706", "38…
$ Fare <dbl> 7.2500, 71.2833, 7.9250, 53.1000, 8.0500, 8.4583, 51.8625, 21.0750, 11.1333, 30.0708, 16.7000, 26.5500, 8.0500, 31.2750, 7.8542, 16.0000, 29.1250, 13.0000, 18.0000, 7.2250, 26.0000,…
$ Cabin <chr> "", "C85", "", "C123", "", "", "E46", "", "", "", "G6", "C103", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "D56", "", "A6", "", "", "", "C23 C25 C27", "", "", "", "B78", "", "", "", "", ""…
$ Embarked <chr> "S", "C", "S", "S", "S", "Q", "S", "S", "S", "C", "S", "S", "S", "S", "S", "S", "Q", "S", "S", "C", "S", "S", "Q", "S", "S", "S", "C", "S", "Q", "S", "C", "C", "Q", "S", "C", "S", "…
$ FamSize <int> 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 4, 2, 1, 2, 0, 0, 6, 0, 0, 5, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 4, 6, 0, 5, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 2, 1, 1, 1, 0, 3, 0, 0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 5, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 3, 7, 0…# 3. Select Variables used for Analysis
titanic1 <- titanic %>%
dplyr::select(Survived, Pclass, Sex, Age, Fare, FamSize) # 분석에 사용할 변수 선택
glimpse(titanic1) # 데이터 구조 확인Rows: 891
Columns: 6
$ Survived <fct> no, yes, yes, yes, no, no, no, no, yes, yes, yes, yes, no, no, no, yes, no, yes, no, yes, no, yes, yes, yes, no, yes, no, no, yes, no, no, yes, yes, no, no, no, yes, no, no, yes, no…
$ Pclass <fct> 3, 1, 3, 1, 3, 3, 1, 3, 3, 2, 3, 1, 3, 3, 3, 2, 3, 2, 3, 3, 2, 2, 3, 1, 3, 3, 3, 1, 3, 3, 1, 1, 3, 2, 1, 1, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 2, 3, 2, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 1, 2, 1, 1, 2, 3, 2, 3, 3…
$ Sex <fct> male, female, female, female, male, male, male, male, female, female, female, female, male, male, female, female, male, male, female, female, male, male, female, male, female, femal…
$ Age <dbl> 22.0, 38.0, 26.0, 35.0, 35.0, NA, 54.0, 2.0, 27.0, 14.0, 4.0, 58.0, 20.0, 39.0, 14.0, 55.0, 2.0, NA, 31.0, NA, 35.0, 34.0, 15.0, 28.0, 8.0, 38.0, NA, 19.0, NA, NA, 40.0, NA, NA, 66.…
$ Fare <dbl> 7.2500, 71.2833, 7.9250, 53.1000, 8.0500, 8.4583, 51.8625, 21.0750, 11.1333, 30.0708, 16.7000, 26.5500, 8.0500, 31.2750, 7.8542, 16.0000, 29.1250, 13.0000, 18.0000, 7.2250, 26.0000,…
$ FamSize <int> 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 4, 2, 1, 2, 0, 0, 6, 0, 0, 5, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 4, 6, 0, 5, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 2, 1, 1, 1, 0, 3, 0, 0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 5, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 3, 7, 0…12.3 데이터 탐색
ggpairs(titanic1,
aes(colour = Survived)) + # Target의 범주에 따라 색깔을 다르게 표현
theme_bw()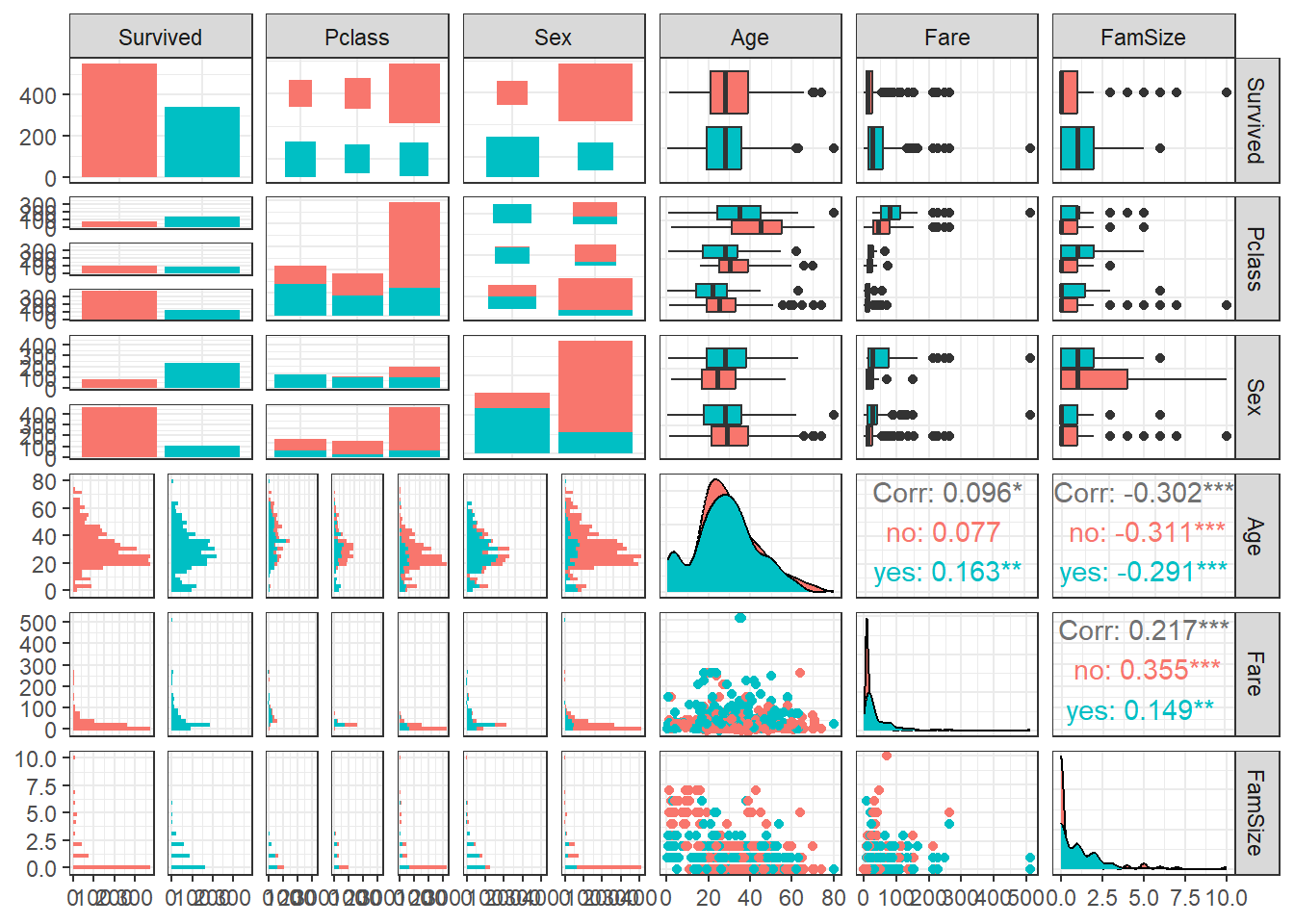
ggpairs(titanic1,
aes(colour = Survived, alpha = 0.8)) + # Target의 범주에 따라 색깔을 다르게 표현
scale_colour_manual(values = c("purple","cyan4")) + # 특정 색깔 지정
scale_fill_manual(values = c("purple","cyan4")) + # 특정 색깔 지정
theme_bw()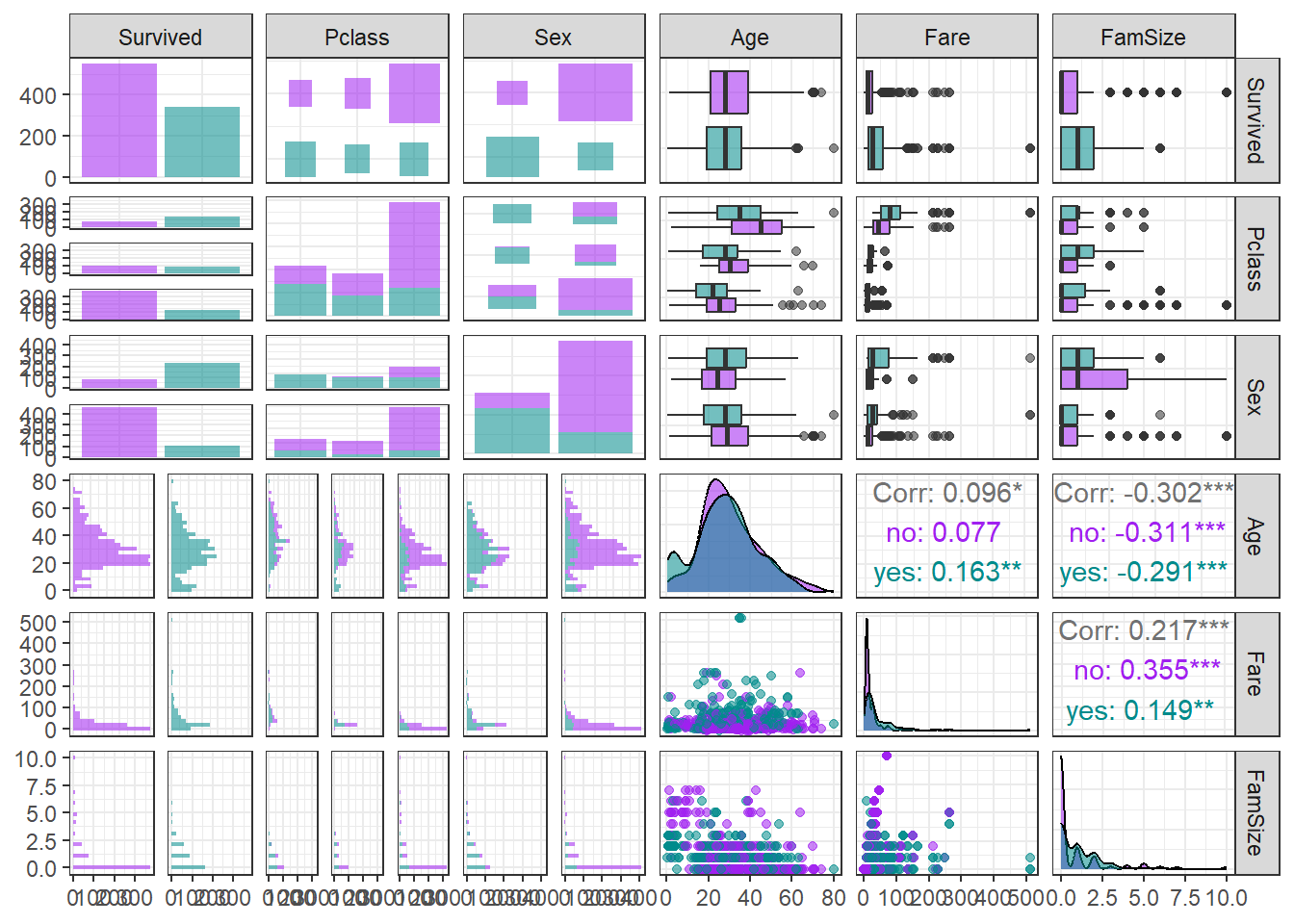
12.4 데이터 분할
# Partition (Training Dataset : Test Dataset = 7:3)
y <- titanic1$Survived # Target
set.seed(200)
ind <- createDataPartition(y, p = 0.7, list =T) # Index를 이용하여 7:3으로 분할
titanic.trd <- titanic1[ind$Resample1,] # Training Dataset
titanic.ted <- titanic1[-ind$Resample1,] # Test Dataset12.5 데이터 전처리 II
# Imputation
titanic.trd.Imp <- titanic.trd %>%
mutate(Age = replace_na(Age, mean(Age, na.rm = TRUE))) # 평균으로 결측값 대체
titanic.ted.Imp <- titanic.ted %>%
mutate(Age = replace_na(Age, mean(titanic.trd$Age, na.rm = TRUE))) # Training Dataset을 이용하여 결측값 대체
glimpse(titanic.trd.Imp) # 데이터 구조 확인Rows: 625
Columns: 6
$ Survived <fct> no, yes, yes, no, no, no, yes, yes, yes, yes, no, no, yes, no, yes, no, yes, no, no, no, yes, no, no, yes, yes, no, no, no, no, no, yes, no, no, no, yes, no, yes, no, no, no, yes, n…
$ Pclass <fct> 3, 3, 1, 3, 3, 3, 3, 2, 3, 1, 3, 3, 2, 3, 3, 2, 1, 3, 3, 1, 3, 3, 1, 1, 3, 2, 1, 1, 3, 3, 3, 3, 2, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 1, 1, 1, 3, 3, 1, 3, 1, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 2, 3, 3, 3, 1, 2, 3…
$ Sex <fct> male, female, female, male, male, male, female, female, female, female, male, female, male, female, female, male, male, female, male, male, female, male, male, female, female, male,…
$ Age <dbl> 22.00000, 26.00000, 35.00000, 35.00000, 29.93737, 2.00000, 27.00000, 14.00000, 4.00000, 58.00000, 39.00000, 14.00000, 29.93737, 31.00000, 29.93737, 35.00000, 28.00000, 8.00000, 29.9…
$ Fare <dbl> 7.2500, 7.9250, 53.1000, 8.0500, 8.4583, 21.0750, 11.1333, 30.0708, 16.7000, 26.5500, 31.2750, 7.8542, 13.0000, 18.0000, 7.2250, 26.0000, 35.5000, 21.0750, 7.2250, 263.0000, 7.8792,…
$ FamSize <int> 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 4, 2, 1, 2, 0, 6, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 4, 0, 5, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 2, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 2, 1, 5, 1, 1, 0, 7, 0, 0, 5, 0, 2, 7, 1, 0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 3…glimpse(titanic.ted.Imp) # 데이터 구조 확인Rows: 266
Columns: 6
$ Survived <fct> yes, no, no, yes, no, yes, yes, yes, yes, yes, no, no, yes, yes, no, yes, no, yes, yes, no, yes, no, no, no, no, no, no, yes, yes, no, no, no, no, no, no, no, no, no, no, yes, no, n…
$ Pclass <fct> 1, 1, 3, 2, 3, 2, 3, 3, 3, 2, 3, 3, 2, 2, 3, 2, 1, 3, 2, 3, 3, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 3, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 2, 3, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 2, 1, 3, 1, 3, 2, 1, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 1, 3, 1, 3…
$ Sex <fct> female, male, male, female, male, male, female, female, male, female, male, male, female, female, male, female, male, male, female, male, female, male, male, male, male, male, male,…
$ Age <dbl> 38.00000, 54.00000, 20.00000, 55.00000, 2.00000, 34.00000, 15.00000, 38.00000, 29.93737, 3.00000, 29.93737, 21.00000, 29.00000, 21.00000, 28.50000, 5.00000, 45.00000, 29.93737, 29.0…
$ Fare <dbl> 71.2833, 51.8625, 8.0500, 16.0000, 29.1250, 13.0000, 8.0292, 31.3875, 7.2292, 41.5792, 8.0500, 7.8000, 26.0000, 10.5000, 7.2292, 27.7500, 83.4750, 15.2458, 10.5000, 8.1583, 7.9250, …
$ FamSize <int> 1, 0, 0, 0, 5, 0, 0, 6, 0, 3, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 3, 1, 2, 0, 0, 6, 0, 0, 0, 0, 4, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 6, 2, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 5, 2, 5, 0, 5, 0, 4, 0, 6…12.6 모형 훈련
Boosting은 다수의 약한 학습자(간단하면서 성능이 낮은 예측 모형)을 순차적으로 학습하는 앙상블 기법이다. Boosting의 특징은 이전 모형의 오차를 반영하여 다음 모형을 생성하며, 오차를 개선하는 방향으로 학습을 수행한다.
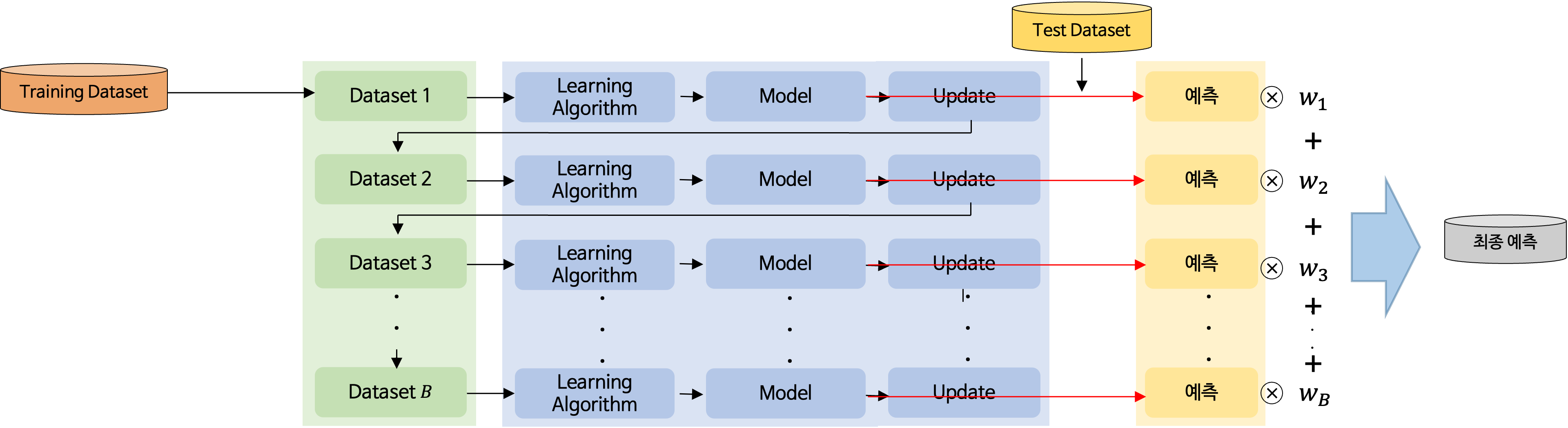
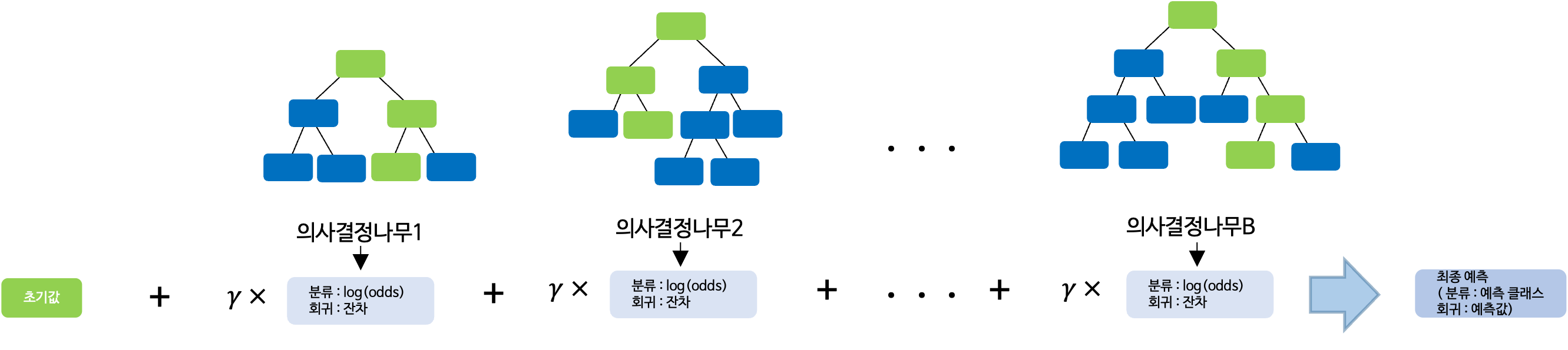
Gradient Boosting은 손실함수를 이용하여 손실함수가 작아지는 방향으로 예측값을 업데이트하며 이전 모형의 오차를 기반으로 다음 모형을 생성한다.

Package "caret"은 통합 API를 통해 R로 기계 학습을 실행할 수 있는 매우 실용적인 방법을 제공한다. Package "caret"에서는 초모수의 최적의 조합을 찾는 방법으로 그리드 검색(Grid Search), 랜덤 검색(Random Search), 직접 탐색 범위 설정이 있다. 여기서는 초모수 shrinkage(학습률), interaction.depth(트리 최대 깊이), n.minobsinnode(터미널 노드의 최소 case 개수), n.trees(트리 개수)의 최적의 조합값을 찾기 위해 그리드 검색을 수행하였고, 이를 기반으로 직접 탐색 범위를 설정하였다. 아래는 그리드 검색을 수행하였을 때 결과이다.
fitControl <- trainControl(method = "cv", number = 5, # 5-Fold Cross Validation (5-Fold CV)
allowParallel = TRUE) # 병렬 처리
set.seed(200) # For CV
gbm.fit <- train(Survived ~ ., data = titanic.trd.Imp,
trControl = fitControl ,
method = "gbm") Iter TrainDeviance ValidDeviance StepSize Improve
1 1.2571 nan 0.1000 0.0343
2 1.2009 nan 0.1000 0.0300
3 1.1562 nan 0.1000 0.0203
4 1.1123 nan 0.1000 0.0209
5 1.0733 nan 0.1000 0.0163
6 1.0433 nan 0.1000 0.0146
7 1.0197 nan 0.1000 0.0109
8 0.9942 nan 0.1000 0.0107
9 0.9759 nan 0.1000 0.0094
10 0.9591 nan 0.1000 0.0072
20 0.8547 nan 0.1000 0.0010
40 0.7710 nan 0.1000 -0.0003
60 0.7328 nan 0.1000 -0.0007
80 0.7089 nan 0.1000 -0.0018
100 0.6875 nan 0.1000 -0.0014
120 0.6671 nan 0.1000 -0.0010
140 0.6472 nan 0.1000 -0.0016
150 0.6410 nan 0.1000 -0.0008Caution! Package "caret"을 통해 "gbm"를 수행하는 경우, 함수 train(Target ~ 예측 변수, data)를 사용하면 범주형 예측 변수는 자동적으로 더미 변환이 된다. 범주형 예측 변수에 대해 더미 변환을 수행하고 싶지 않다면 함수 train(x = 예측 변수만 포함하는 데이터셋, y = Target만 포함하는 데이터셋)를 사용한다.
gbm.fitStochastic Gradient Boosting
625 samples
5 predictor
2 classes: 'no', 'yes'
No pre-processing
Resampling: Cross-Validated (5 fold)
Summary of sample sizes: 500, 500, 500, 500, 500
Resampling results across tuning parameters:
interaction.depth n.trees Accuracy Kappa
1 50 0.8032 0.5687775
1 100 0.7952 0.5619060
1 150 0.7984 0.5674442
2 50 0.8000 0.5696634
2 100 0.7984 0.5665672
2 150 0.8016 0.5732542
3 50 0.8000 0.5628963
3 100 0.8048 0.5781083
3 150 0.8192 0.6138743
Tuning parameter 'shrinkage' was held constant at a value of 0.1
Tuning parameter 'n.minobsinnode' was held constant at a value of 10
Accuracy was used to select the optimal model using the largest value.
The final values used for the model were n.trees = 150, interaction.depth = 3, shrinkage = 0.1 and n.minobsinnode = 10.plot(gbm.fit) # Plot 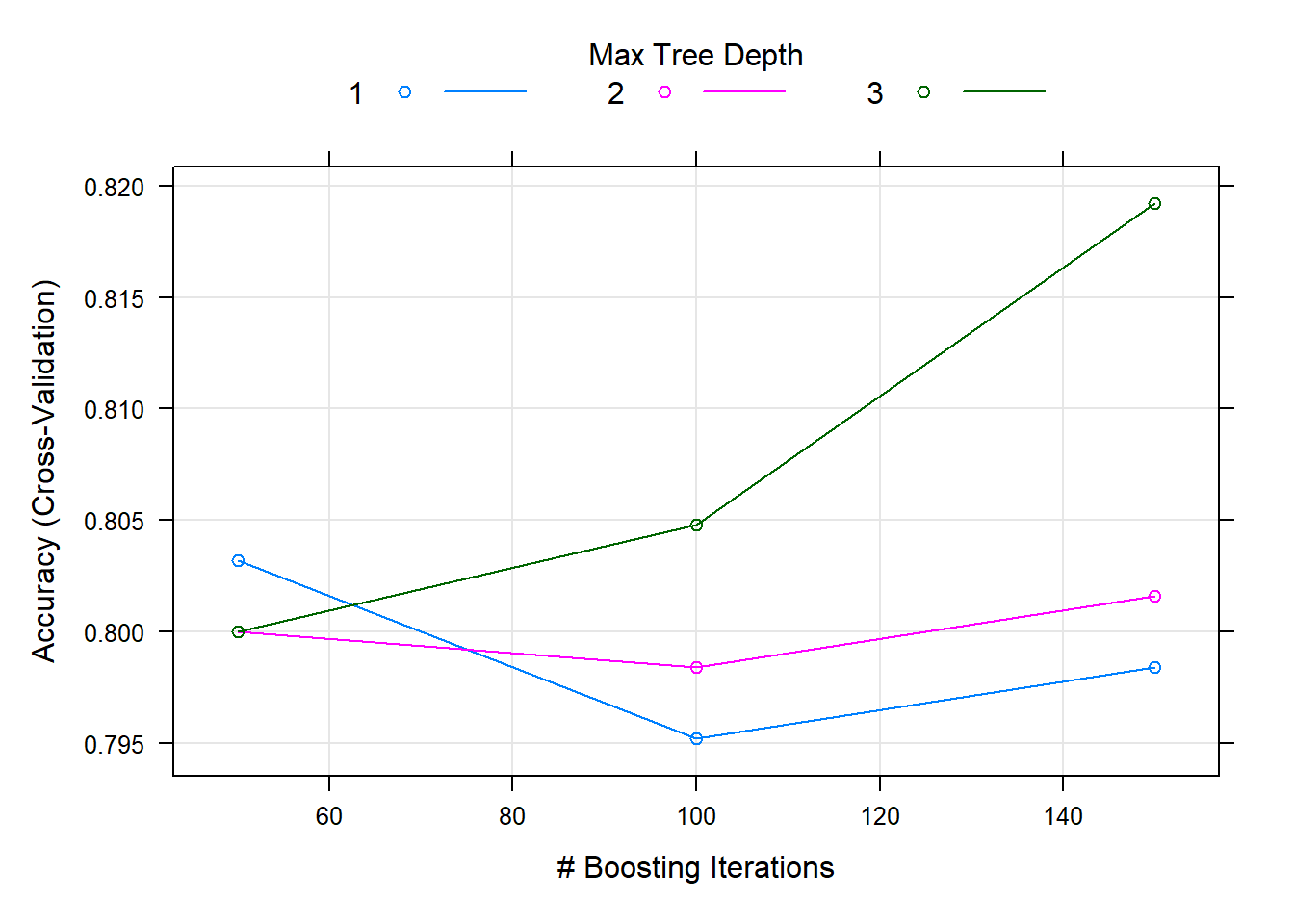
Result! 랜덤하게 결정된 3개의 초모수 interaction.depth, n.trees 값과 1개의 초모수 shrinkage, n.minobsinnode 값을 조합하여 만든 9개의 초모수 조합값 (shrinkage, interaction.depth, n.minobsinnode, n.trees)에 대한 정확도를 보여주며, (shrinkage = 0.1, interaction.depth = 3, n.minobsinnode = 10, n.trees = 150)일 때 정확도가 가장 높은 것을 알 수 있다. 따라서 그리드 검색을 통해 찾은 최적의 초모수 조합값 (shrinkage = 0.1, interaction.depth = 3, n.minobsinnode = 10, n.trees = 150) 근처의 값들을 탐색 범위로 설정하여 훈련을 다시 수행할 수 있다.
customGrid <- expand.grid(shrinkage = seq(0.08, 0.12, by = 0.01), # shrinkage의 탐색 범위
interaction.depth = seq(2, 4, by = 1), # interaction.depth의 탐색 범위
n.minobsinnode = seq(9, 11, by = 1), # n.minobsinnode의 탐색 범위
n.trees = seq(149, 151, by = 1)) # n.trees의 탐색 범위
set.seed(200) # For CV
gbm.tune.fit <- train(Survived ~ ., data = titanic.trd.Imp,
trControl = fitControl ,
method = "gbm",
tuneGrid = customGrid)Iter TrainDeviance ValidDeviance StepSize Improve
1 1.2624 nan 0.0900 0.0373
2 1.2035 nan 0.0900 0.0265
3 1.1574 nan 0.0900 0.0222
4 1.1146 nan 0.0900 0.0216
5 1.0759 nan 0.0900 0.0156
6 1.0451 nan 0.0900 0.0158
7 1.0172 nan 0.0900 0.0118
8 0.9941 nan 0.0900 0.0100
9 0.9726 nan 0.0900 0.0101
10 0.9574 nan 0.0900 0.0057
20 0.8417 nan 0.0900 0.0025
40 0.7541 nan 0.0900 -0.0006
60 0.7059 nan 0.0900 -0.0006
80 0.6752 nan 0.0900 -0.0012
100 0.6570 nan 0.0900 -0.0021
120 0.6309 nan 0.0900 -0.0012
140 0.6089 nan 0.0900 -0.0005
150 0.5981 nan 0.0900 -0.0013gbm.tune.fitStochastic Gradient Boosting
625 samples
5 predictor
2 classes: 'no', 'yes'
No pre-processing
Resampling: Cross-Validated (5 fold)
Summary of sample sizes: 500, 500, 500, 500, 500
Resampling results across tuning parameters:
shrinkage interaction.depth n.minobsinnode n.trees Accuracy Kappa
0.08 2 9 149 0.7952 0.5591812
0.08 2 9 150 0.7952 0.5591812
0.08 2 9 151 0.7952 0.5593732
0.08 2 10 149 0.8016 0.5734456
0.08 2 10 150 0.7984 0.5656913
0.08 2 10 151 0.7968 0.5627190
0.08 2 11 149 0.7984 0.5632410
0.08 2 11 150 0.7952 0.5564770
0.08 2 11 151 0.7952 0.5573275
0.08 3 9 149 0.8208 0.6144630
0.08 3 9 150 0.8192 0.6115500
0.08 3 9 151 0.8224 0.6171112
0.08 3 10 149 0.8144 0.5997213
0.08 3 10 150 0.8128 0.5968501
0.08 3 10 151 0.8128 0.5985971
0.08 3 11 149 0.8080 0.5870642
0.08 3 11 150 0.8080 0.5863755
0.08 3 11 151 0.8096 0.5901226
0.08 4 9 149 0.8176 0.6062555
0.08 4 9 150 0.8176 0.6070349
0.08 4 9 151 0.8128 0.5962777
0.08 4 10 149 0.8128 0.5972400
0.08 4 10 150 0.8080 0.5871991
0.08 4 10 151 0.8096 0.5909302
0.08 4 11 149 0.8144 0.6012404
0.08 4 11 150 0.8160 0.6045500
0.08 4 11 151 0.8176 0.6071129
0.09 2 9 149 0.8064 0.5845136
0.09 2 9 150 0.8096 0.5909709
0.09 2 9 151 0.8080 0.5877708
0.09 2 10 149 0.8128 0.5946760
0.09 2 10 150 0.8128 0.5940690
0.09 2 10 151 0.8176 0.6040105
0.09 2 11 149 0.8064 0.5817456
0.09 2 11 150 0.8032 0.5744295
0.09 2 11 151 0.8048 0.5779296
0.09 3 9 149 0.8176 0.6050779
0.09 3 9 150 0.8176 0.6056842
0.09 3 9 151 0.8160 0.6018222
0.09 3 10 149 0.8176 0.6042407
0.09 3 10 150 0.8160 0.6011866
0.09 3 10 151 0.8208 0.6117746
0.09 3 11 149 0.8192 0.6114804
0.09 3 11 150 0.8176 0.6082544
0.09 3 11 151 0.8208 0.6152589
0.09 4 9 149 0.8192 0.6153226
0.09 4 9 150 0.8192 0.6152896
0.09 4 9 151 0.8176 0.6101179
0.09 4 10 149 0.8240 0.6223660
0.09 4 10 150 0.8176 0.6095809
0.09 4 10 151 0.8192 0.6126612
0.09 4 11 149 0.8272 0.6264772
0.09 4 11 150 0.8288 0.6304270
0.09 4 11 151 0.8256 0.6228076
0.10 2 9 149 0.8048 0.5811582
0.10 2 9 150 0.8048 0.5818748
0.10 2 9 151 0.8032 0.5781233
0.10 2 10 149 0.8016 0.5739252
0.10 2 10 150 0.8000 0.5688869
0.10 2 10 151 0.8016 0.5720188
0.10 2 11 149 0.8080 0.5859403
0.10 2 11 150 0.8048 0.5799433
0.10 2 11 151 0.8064 0.5829712
0.10 3 9 149 0.8160 0.6022133
0.10 3 9 150 0.8176 0.6052717
0.10 3 9 151 0.8208 0.6126740
0.10 3 10 149 0.8096 0.5958014
0.10 3 10 150 0.8064 0.5882751
0.10 3 10 151 0.8096 0.5950331
0.10 3 11 149 0.8208 0.6162759
0.10 3 11 150 0.8176 0.6098820
0.10 3 11 151 0.8144 0.6029499
0.10 4 9 149 0.8128 0.5999040
0.10 4 9 150 0.8048 0.5826735
0.10 4 9 151 0.8080 0.5883021
0.10 4 10 149 0.8224 0.6178314
0.10 4 10 150 0.8240 0.6222348
0.10 4 10 151 0.8256 0.6253934
0.10 4 11 149 0.8224 0.6196381
0.10 4 11 150 0.8224 0.6197772
0.10 4 11 151 0.8208 0.6160745
0.11 2 9 149 0.8096 0.5937889
0.11 2 9 150 0.8112 0.5968405
0.11 2 9 151 0.8112 0.5968405
0.11 2 10 149 0.8048 0.5786148
0.11 2 10 150 0.8064 0.5816521
0.11 2 10 151 0.8032 0.5748027
0.11 2 11 149 0.8096 0.5878849
0.11 2 11 150 0.8128 0.5956412
0.11 2 11 151 0.8080 0.5839207
0.11 3 9 149 0.8192 0.6137125
0.11 3 9 150 0.8144 0.6023771
0.11 3 9 151 0.8192 0.6144973
0.11 3 10 149 0.8144 0.5991862
0.11 3 10 150 0.8128 0.5954511
0.11 3 10 151 0.8144 0.5999162
0.11 3 11 149 0.8096 0.5904760
0.11 3 11 150 0.8048 0.5800811
0.11 3 11 151 0.8080 0.5875993
0.11 4 9 149 0.8096 0.5906864
0.11 4 9 150 0.8064 0.5842011
0.11 4 9 151 0.8096 0.5915463
0.11 4 10 149 0.8144 0.5995659
0.11 4 10 150 0.8176 0.6061575
0.11 4 10 151 0.8176 0.6061295
0.11 4 11 149 0.8256 0.6249168
0.11 4 11 150 0.8256 0.6254403
0.11 4 11 151 0.8208 0.6143930
0.12 2 9 149 0.8016 0.5722035
0.12 2 9 150 0.8000 0.5693195
0.12 2 9 151 0.8000 0.5711099
0.12 2 10 149 0.8128 0.5970680
0.12 2 10 150 0.8096 0.5887563
0.12 2 10 151 0.8144 0.5992358
0.12 2 11 149 0.8096 0.5888815
0.12 2 11 150 0.8096 0.5880570
0.12 2 11 151 0.8048 0.5781171
0.12 3 9 149 0.8176 0.6072785
0.12 3 9 150 0.8224 0.6176963
0.12 3 9 151 0.8144 0.6003575
0.12 3 10 149 0.8144 0.5984722
0.12 3 10 150 0.8160 0.6015585
0.12 3 10 151 0.8144 0.5985069
0.12 3 11 149 0.8192 0.6106743
0.12 3 11 150 0.8144 0.5993903
0.12 3 11 151 0.8096 0.5893437
0.12 4 9 149 0.8080 0.5875854
0.12 4 9 150 0.8096 0.5923086
0.12 4 9 151 0.8128 0.5989533
0.12 4 10 149 0.8144 0.5981933
0.12 4 10 150 0.8112 0.5920172
0.12 4 10 151 0.8128 0.5957502
0.12 4 11 149 0.8128 0.6003945
0.12 4 11 150 0.8176 0.6096983
0.12 4 11 151 0.8128 0.5989083
Accuracy was used to select the optimal model using the largest value.
The final values used for the model were n.trees = 150, interaction.depth = 4, shrinkage = 0.09 and n.minobsinnode = 11.plot(gbm.tune.fit) # Plot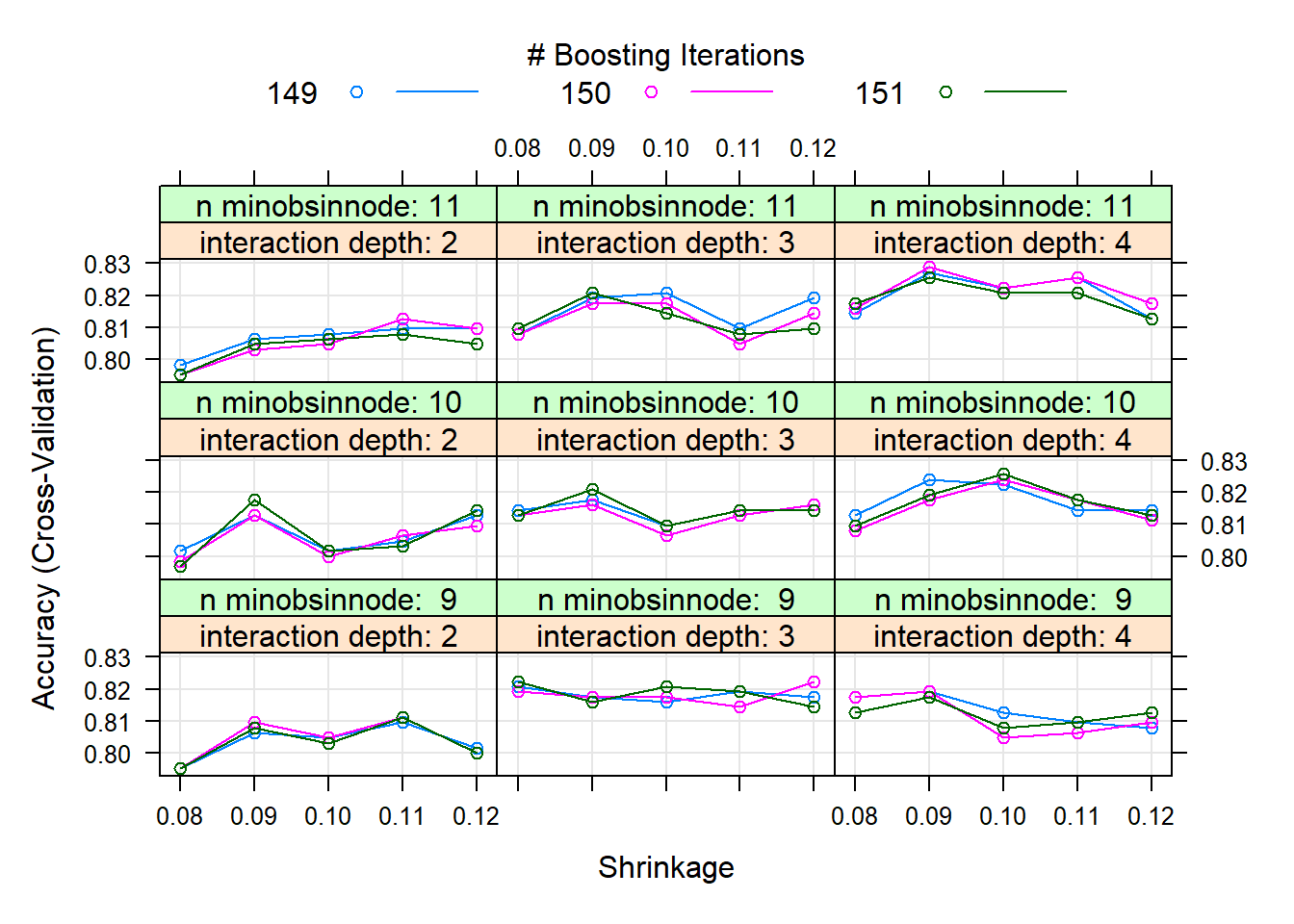
gbm.tune.fit$bestTune # 최적의 초모수 조합값 n.trees interaction.depth shrinkage n.minobsinnode
53 150 4 0.09 11Result! (shrinkage = 0.09, interaction.depth = 4, n.minobsinnode = 11, n.trees = 150)일 때 정확도가 가장 높은 것을 알 수 있으며, (shrinkage = 0.09, interaction.depth = 4, n.minobsinnode = 11, n.trees = 150)를 가지는 모형을 최적의 훈련된 모형으로 선택한다.
# 변수 중요도
summary(gbm.tune.fit$finalModel, las = 2) 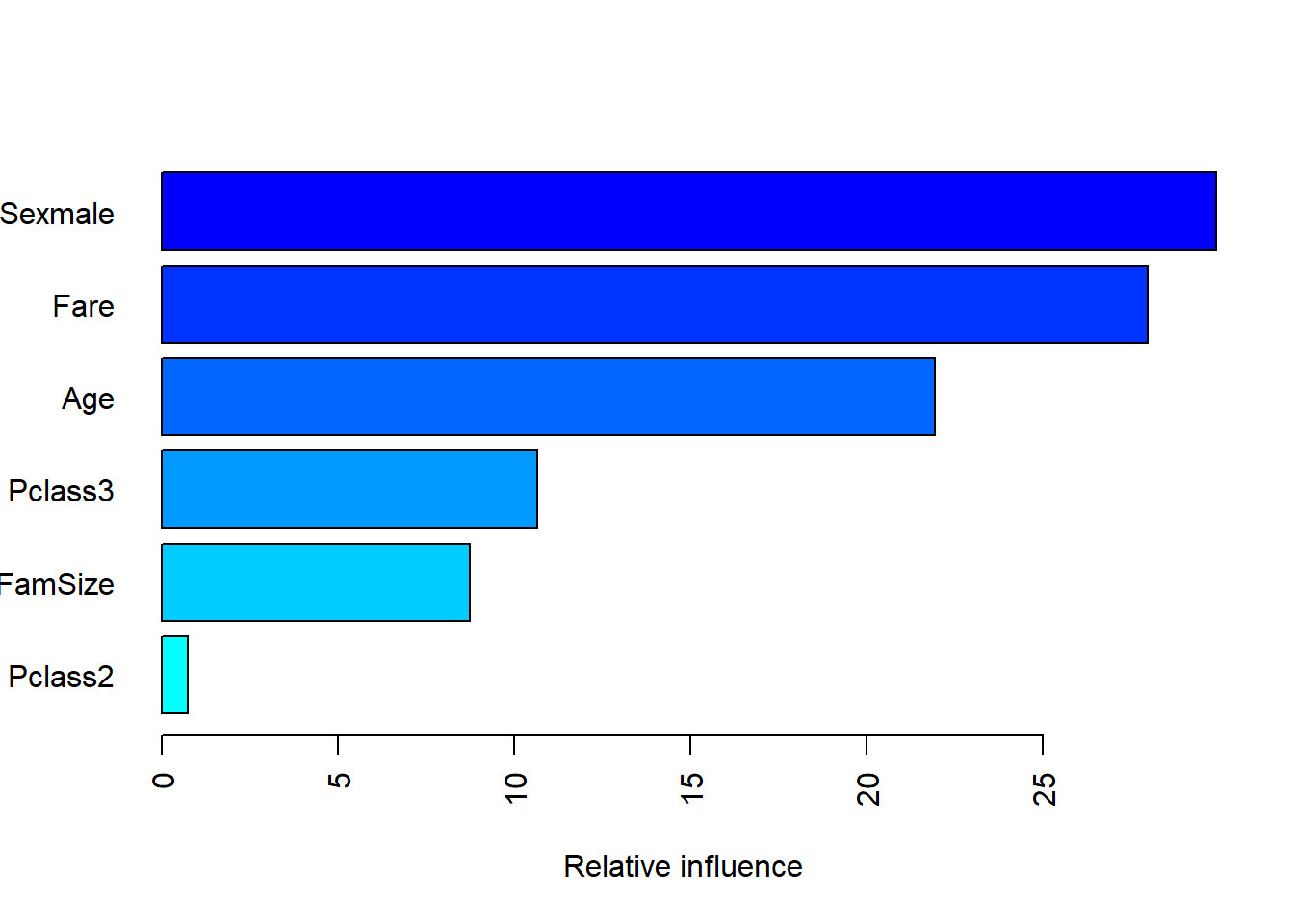
var rel.inf
Sexmale Sexmale 29.9231815
Fare Fare 27.9787356
Age Age 21.9393972
Pclass3 Pclass3 10.6516698
FamSize FamSize 8.7607672
Pclass2 Pclass2 0.7462487Result! 변수 Sexmale이 Target Survived을 분류하는 데 있어 중요하다.
12.7 모형 평가
Caution! 모형 평가를 위해 Test Dataset에 대한 예측 class/확률 이 필요하며, 함수 predict()를 이용하여 생성한다.
# 예측 class 생성
test.gbm.class <- predict(gbm.tune.fit,
newdata = titanic.ted.Imp[,-1]) # Test Dataset including Only 예측 변수
test.gbm.class [1] yes no no yes no no no no no yes no no yes yes no yes no no yes no no no no no no no no no yes no yes no no no no no no no no yes no no no yes no no no no
[49] yes no no no no no no yes no no no yes no no yes no yes no no no no no no no no yes no no no no no yes yes no yes no no no no no no no no no no yes yes yes
[97] yes yes no no no yes yes no no yes no yes no yes yes no yes no yes no yes no no no yes no no yes no no yes yes no yes no yes no no yes yes no no no no yes no no no
[145] yes no no no no no no yes no no no no no no no no yes no yes yes no yes yes no no no no no yes yes yes no yes no no no no no no yes no no no yes no yes no no
[193] no no no yes no no no no no yes no no no no no no yes no no yes yes no no no yes yes no no no no no yes yes yes no no no no no no no no yes no no yes no no
[241] no yes no no no yes no yes no no yes no no no no yes yes yes no yes no yes yes no no no
Levels: no yes12.7.1 ConfusionMatrix
CM <- caret::confusionMatrix(test.gbm.class, titanic.ted.Imp$Survived,
positive = "yes") # confusionMatrix(예측 class, 실제 class, positive = "관심 class")
CMConfusion Matrix and Statistics
Reference
Prediction no yes
no 155 32
yes 9 70
Accuracy : 0.8459
95% CI : (0.7968, 0.8871)
No Information Rate : 0.6165
P-Value [Acc > NIR] : < 2.2e-16
Kappa : 0.6595
Mcnemar's Test P-Value : 0.0005908
Sensitivity : 0.6863
Specificity : 0.9451
Pos Pred Value : 0.8861
Neg Pred Value : 0.8289
Prevalence : 0.3835
Detection Rate : 0.2632
Detection Prevalence : 0.2970
Balanced Accuracy : 0.8157
'Positive' Class : yes
12.7.2 ROC 곡선
# 예측 확률 생성
test.gbm.prob <- predict(gbm.tune.fit,
newdata = titanic.ted.Imp[,-1],# Test Dataset including Only 예측 변수
type = "prob") # 예측 확률 생성
test.gbm.prob %>%
as_tibble# A tibble: 266 × 2
no yes
<dbl> <dbl>
1 0.0427 0.957
2 0.764 0.236
3 0.922 0.0776
4 0.125 0.875
5 0.649 0.351
6 0.842 0.158
7 0.510 0.490
8 0.943 0.0569
9 0.944 0.0555
10 0.0294 0.971
# ℹ 256 more rowstest.gbm.prob <- test.gbm.prob[,2] # "Survived = yes"에 대한 예측 확률
ac <- titanic.ted.Imp$Survived # Test Dataset의 실제 class
pp <- as.numeric(test.gbm.prob) # 예측 확률을 수치형으로 변환12.7.2.1 Package “pROC”
pacman::p_load("pROC")
gbm.roc <- roc(ac, pp, plot = T, col = "gray") # roc(실제 class, 예측 확률)
auc <- round(auc(gbm.roc), 3)
legend("bottomright", legend = auc, bty = "n")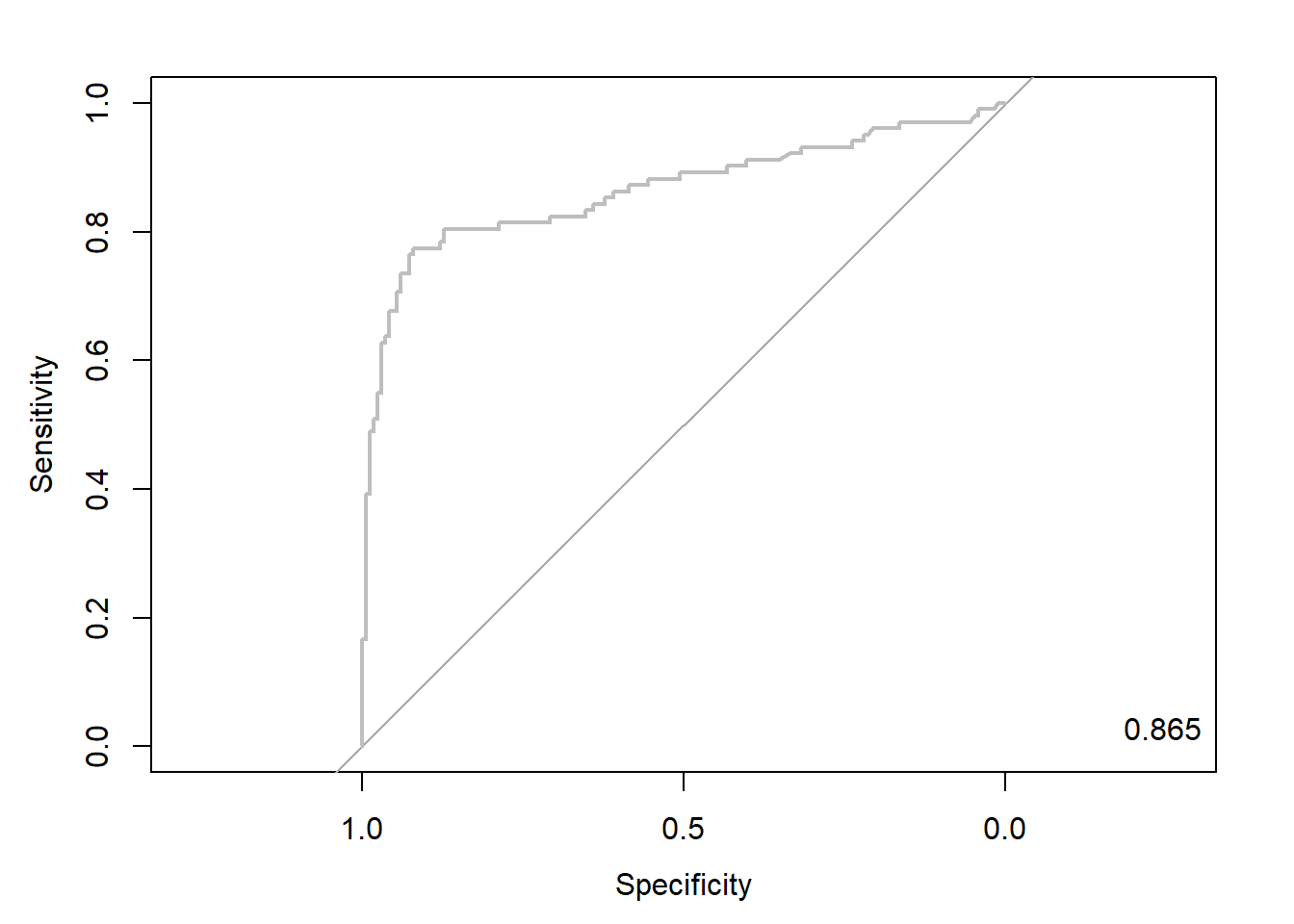
Caution! Package "pROC"를 통해 출력한 ROC 곡선은 다양한 함수를 이용해서 그래프를 수정할 수 있다.
# 함수 plot.roc() 이용
plot.roc(gbm.roc,
col="gray", # Line Color
print.auc = TRUE, # AUC 출력 여부
print.auc.col = "red", # AUC 글씨 색깔
print.thres = TRUE, # Cutoff Value 출력 여부
print.thres.pch = 19, # Cutoff Value를 표시하는 도형 모양
print.thres.col = "red", # Cutoff Value를 표시하는 도형의 색깔
auc.polygon = TRUE, # 곡선 아래 면적에 대한 여부
auc.polygon.col = "gray90") # 곡선 아래 면적의 색깔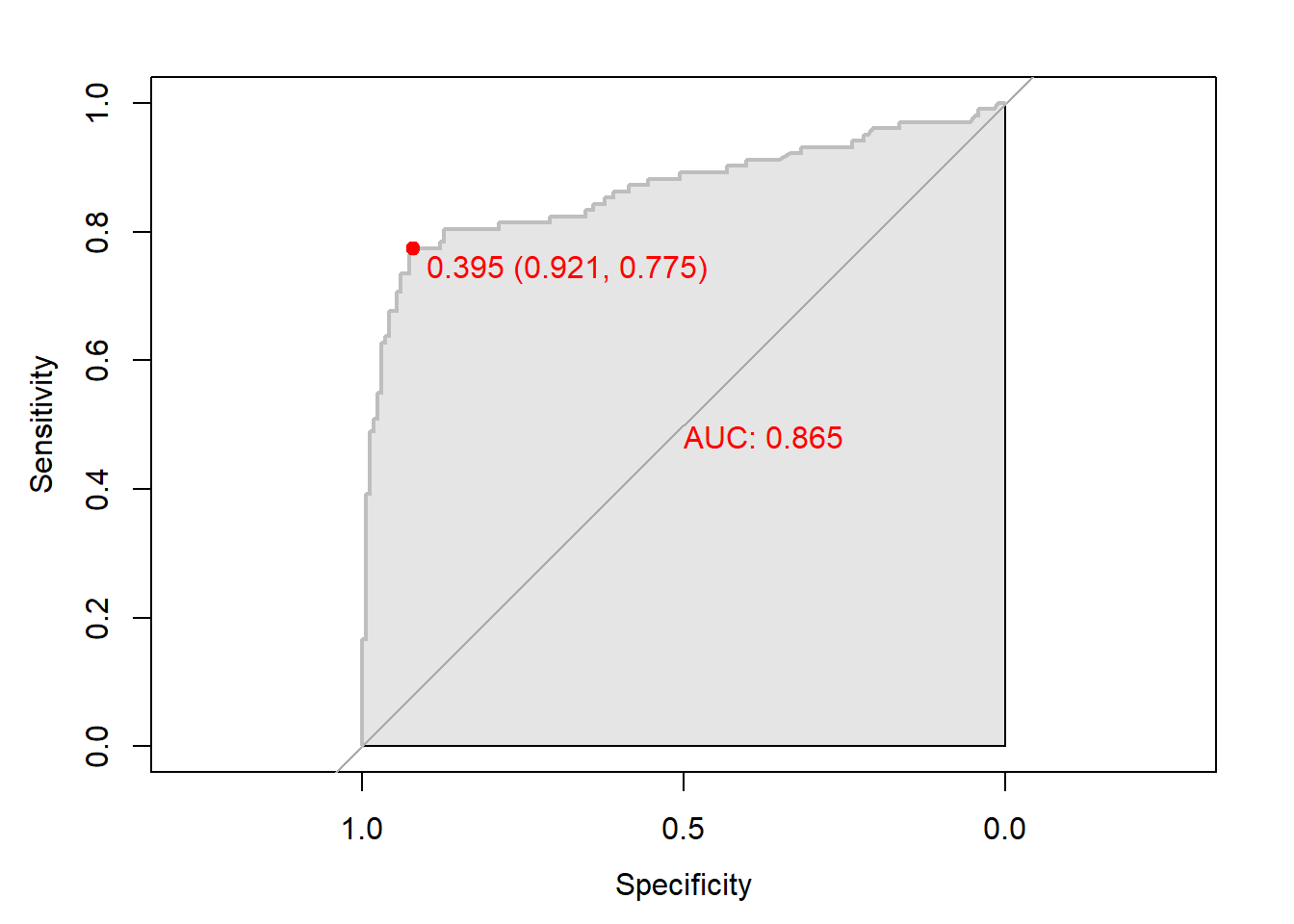
# 함수 ggroc() 이용
ggroc(gbm.roc) +
annotate(geom = "text", x = 0.9, y = 1.0,
label = paste("AUC = ", auc),
size = 5,
color="red") +
theme_bw()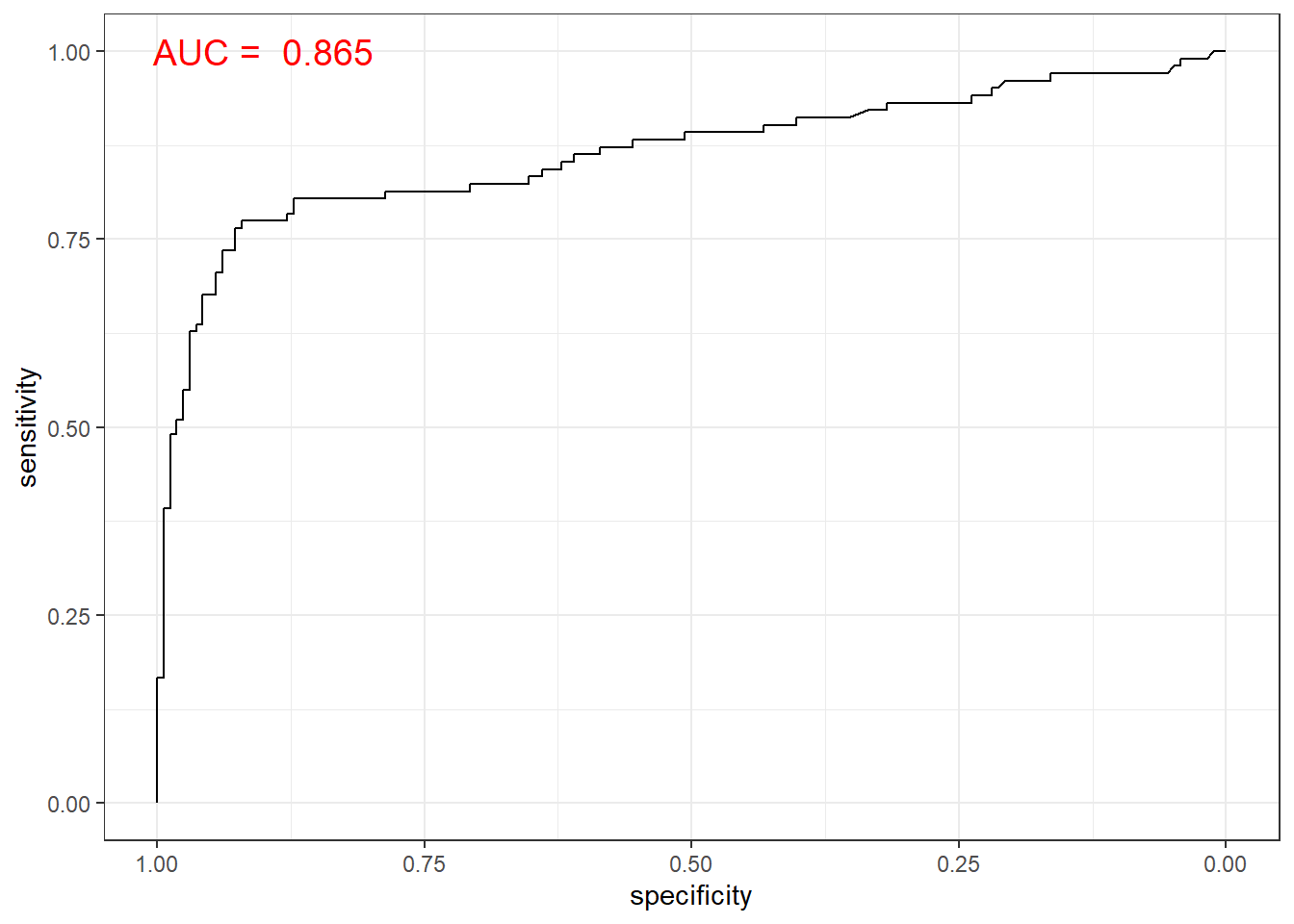
12.7.2.2 Package “Epi”
pacman::p_load("Epi")
# install_version("etm", version = "1.1", repos = "http://cran.us.r-project.org")
ROC(pp, ac, plot = "ROC") # ROC(예측 확률, 실제 class) 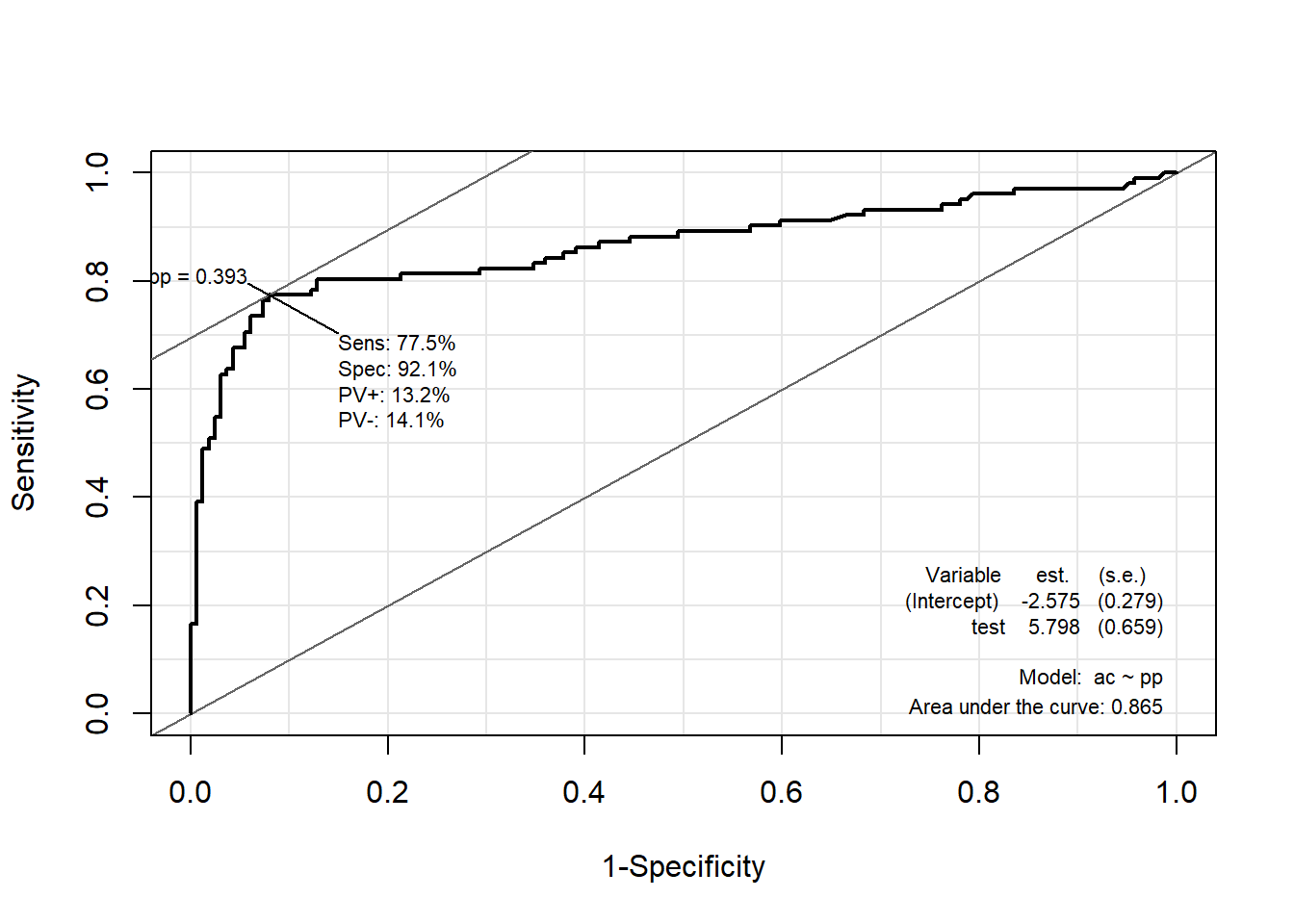
12.7.2.3 Package “ROCR”
pacman::p_load("ROCR")
gbm.pred <- prediction(pp, ac) # prediction(예측 확률, 실제 class)
gbm.perf <- performance(gbm.pred, "tpr", "fpr") # performance(, "민감도", "1-특이도")
plot(gbm.perf, col = "gray") # ROC Curve
perf.auc <- performance(gbm.pred, "auc") # AUC
auc <- attributes(perf.auc)$y.values
legend("bottomright", legend = auc, bty = "n")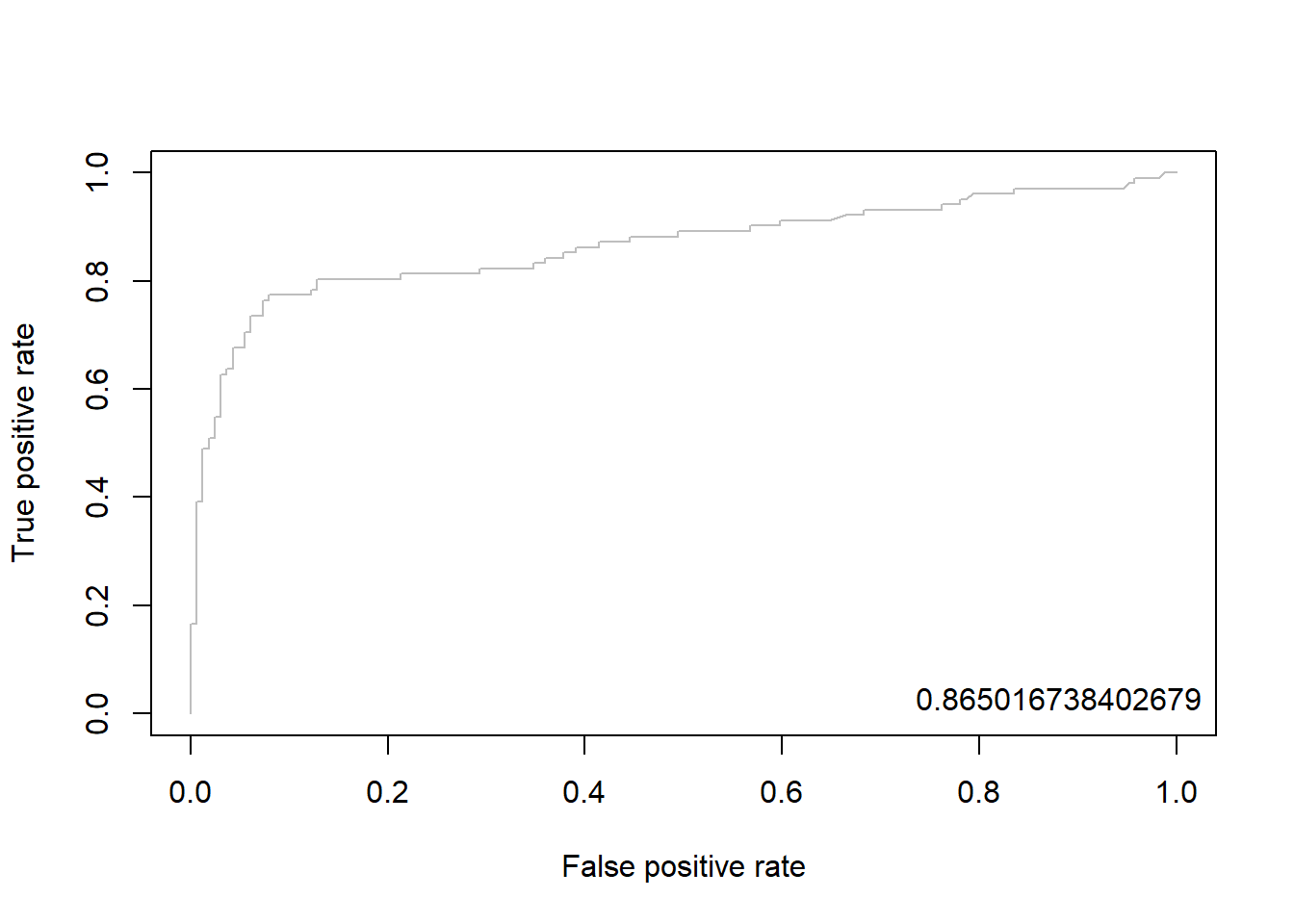
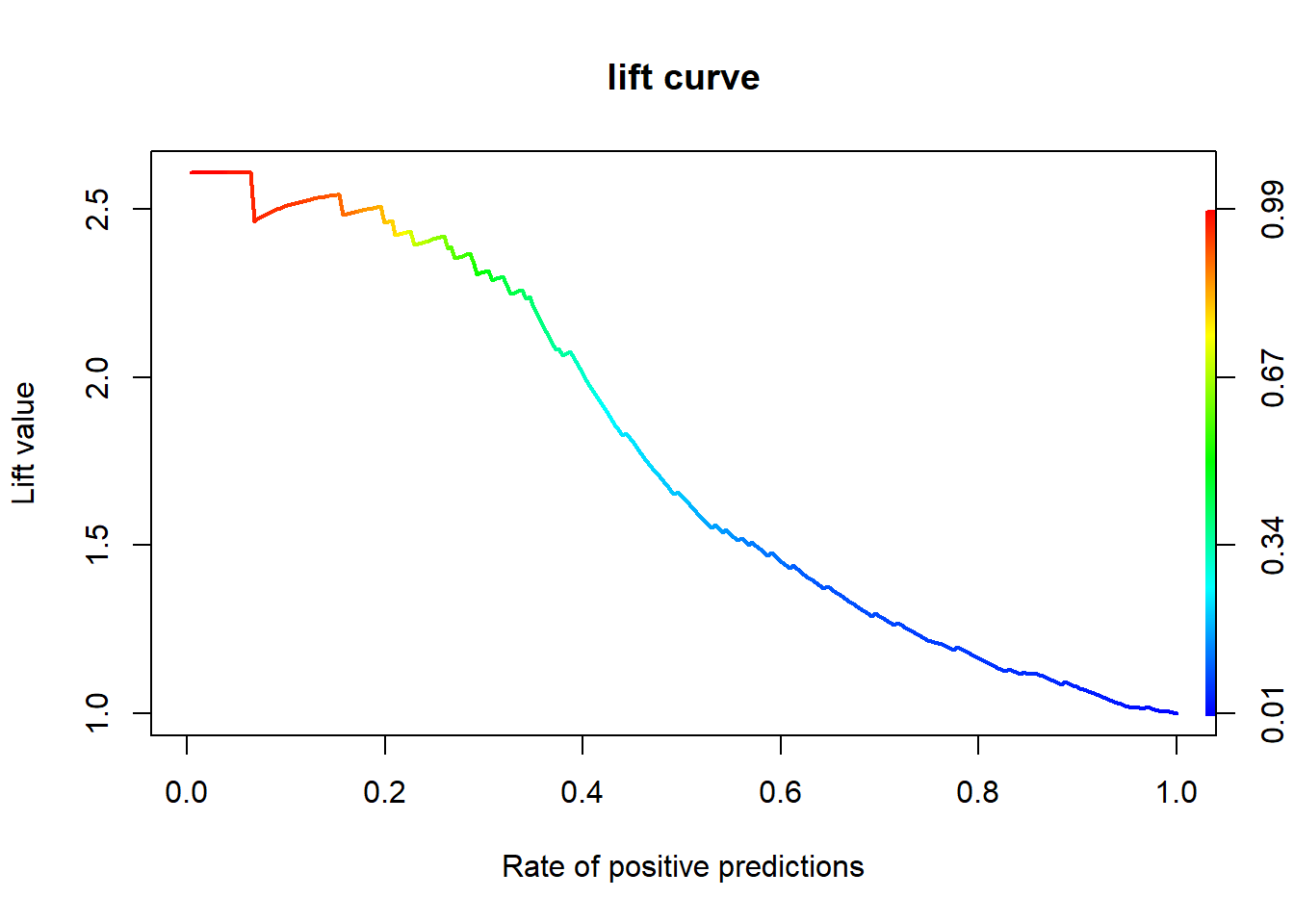
12.7.3 향상 차트
12.7.3.1 Package “ROCR”
gbm.perf <- performance(gbm.pred, "lift", "rpp") # Lift Chart
plot(gbm.perf, main = "lift curve",
colorize = T, # Coloring according to cutoff
lwd = 2)